Compression vs absorption refrigeration: it’s time to explore the world of cooling systems! Let’s dig deep into the differences and similarities of these two methods, and see which one might be right for your home. Ready to chill out? Let’s dive in!
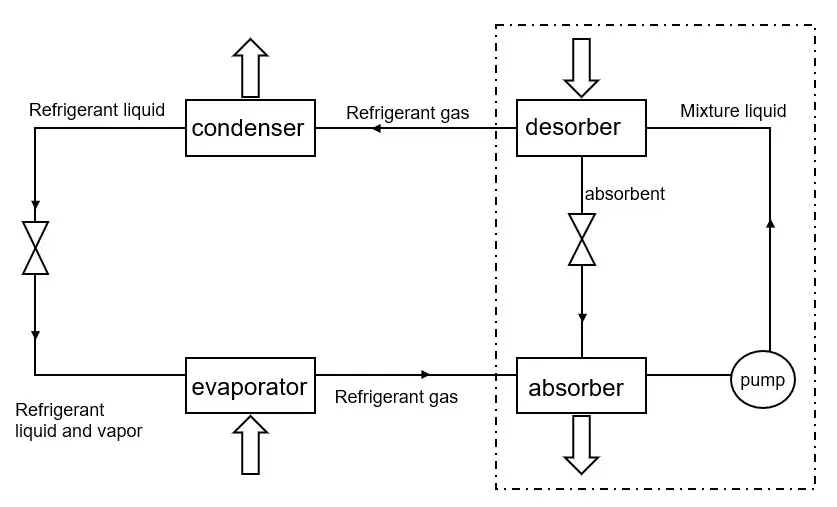
Table of Contents
Definition of Refrigeration Systems
So, what are refrigeration systems? Simply put, they’re devices that remove heat from an enclosed space, helping to maintain a lower temperature than the surrounding environment. Cool, huh?
Purpose and Applications
These systems have a variety of uses, from keeping our food fresh to making our homes comfortable during sweltering summers. You might even say they’re the unsung heroes of modern living!
Basic Components
Though there are many types of refrigeration systems, most have some common components: a refrigerant, a heat exchanger, and a compressor or absorber. We’ll dive into the specifics in just a bit.
Compression and Absorption Refrigeration
Now, let’s talk about the two main types of refrigeration systems: compression and absorption. How do they work, and what makes them different?
Overview of Compression Refrigeration
Compression refrigeration uses a compressor to pump refrigerant through the system, transferring heat from one place to another. It’s the most common type of cooling system found in homes and commercial spaces.
Overview of Absorption Refrigeration
Absorption refrigeration, on the other hand, uses a chemical process to absorb and release heat. It’s less common, but you’ll still find it in some niche applications, like RVs and industrial settings.
To read more in-depth articles, click here: Absorption Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Understanding It
Compression Refrigeration
Vapor Compression Cycle
Let’s take a closer look at the star of the show, the vapor compression cycle. This four-step process is what makes compression refrigeration tick.
Basic Components
Here are the key players in a compression refrigeration system:
Compressor
This is the “engine” that drives the refrigeration cycle by compressing the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature.
Condenser
The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas releases its heat to the environment, turning it into a cooler liquid.
Expansion Valve
This valve reduces the pressure of the refrigerant liquid, allowing it to expand and cool further.
Evaporator
The refrigerant absorbs heat from the space to be cooled, turning it back into a low-pressure gas that returns to the compressor.
Phases of the Vapor Compression Cycle
Here’s how the magic happens:
Compression
The compressor squeezes the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature. It’s like when you pump air into a bicycle tire, and the pump gets hot!
Condensation
As the hot refrigerant gas flows through the condenser, it releases heat to the surrounding air, transforming into a cooler liquid.
Expansion
The refrigerant liquid passes through the expansion valve, reducing its pressure and causing it to expand and cool down even more.
Evaporation
Finally, the cold refrigerant absorbs heat from the space to be cooled in the evaporator, turning back into a low-pressure gas, ready for another trip through the cycle.
Efficiency and Performance
Now, let’s talk about the efficiency of compression refrigeration systems. How do we measure it, and what factors can influence their performance?
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a measure of a refrigeration system’s efficiency. It’s the ratio of cooling power to energy input. Higher COP means better efficiency, and who doesn’t love saving on energy bills, right?
Factors Affecting Efficiency
Here are some things that can impact a compression refrigeration system’s efficiency:
Temperature Lift
The difference between the evaporator and condenser temperatures plays a crucial role. Greater temperature lifts require more energy, reducing efficiency.
Refrigerant Choice
The type of refrigerant used can also affect performance. Some refrigerants are more efficient than others, but they may have environmental drawbacks. It’s a delicate balance!
System Design
Lastly, the design of the refrigeration system itself can impact efficiency. Better components and optimized designs can lead to improved performance.
Absorption Refrigeration
Absorption Refrigeration Cycle
Now let’s explore absorption refrigeration, the quieter cousin of compression refrigeration. This system uses a different process, but with the same goal: keeping things cool.
Basic Components
Here’s a rundown of the main parts in an absorption refrigeration system:
Generator
This component heats a solution of refrigerant and absorbent, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and separate from the absorbent.
Absorber
The absorbent collects the evaporated refrigerant, creating a low-pressure environment that drives the refrigeration cycle.
Condenser
Similar to the compression system, the condenser cools the refrigerant vapor, turning it into a liquid.
Expansion Valve
Again, like in the compression system, the expansion valve reduces the pressure of the refrigerant liquid, allowing it to expand and cool further.
Evaporator
The cold refrigerant absorbs heat from the space to be cooled and evaporates, repeating the cycle.
Phases of the Absorption Cycle
Let’s break down the steps of the absorption refrigeration process:
Generation
The generator heats the refrigerant-absorbent solution, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and separate from the absorbent. It’s like boiling water to make tea!
Absorption
The absorbent in the absorber collects the evaporated refrigerant, creating a low-pressure environment that drives the refrigeration cycle forward.
Condensation
The refrigerant vapor flows through the condenser, releasing heat and transforming into a liquid.
Expansion
As the refrigerant liquid passes through the expansion valve, its pressure drops, allowing it to expand and cool down.
Evaporation
In the evaporator, the cold refrigerant absorbs heat from the space to be cooled and evaporates, ready to start the cycle anew.
Absorption Fridge Efficiency
So, how efficient are absorption refrigeration systems? Let’s find out!
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
Just like with compression refrigeration, we use the Coefficient of Performance (COP) to measure efficiency in absorption systems. But generally, absorption refrigeration has a lower COP compared to compression systems.
Factors Affecting Efficiency
Here’s what can impact the efficiency of an absorption refrigeration system:
Temperature Lift
As with compression systems, a greater temperature lift means reduced efficiency. It’s important to find the right balance!
Absorbent-Refrigerant Pair
The choice of absorbent and refrigerant can significantly affect the system’s performance. Some pairs work better together than others, like a well-choreographed dance duo!
System Design
And, of course, the overall design of the system can make a difference. A well-designed absorption refrigeration system can help improve its efficiency.
Comparison: Vapor Compression vs Absorption Refrigeration
Efficiency and Performance
When it comes to efficiency and performance, compression refrigeration systems generally come out on top, boasting higher COP values. However, absorption refrigeration has its advantages, like quiet operation and the ability to utilize waste heat.
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
As mentioned earlier, compression systems typically have higher COP values compared to absorption systems, making them more energy-efficient.
Energy Consumption
Due to their higher efficiency, compression refrigeration systems tend to consume less energy than absorption systems. But remember, absorption systems can take advantage of waste heat, which can be a big plus!
Environmental Impact
Compression refrigeration systems often use synthetic refrigerants that can harm the environment, while absorption systems typically use natural refrigerants. However, the lower efficiency of absorption systems may result in higher energy consumption, depending on the application.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Let’s summarize the advantages and disadvantages of compression refrigeration
Advantages of Compression Refrigeration
High Efficiency
- Compression systems generally have higher COP values, making them more energy-efficient.
Flexibility in Capacity
- These systems can be easily scaled to meet various cooling needs.
Rapid Cooling
- Compression refrigeration systems can achieve rapid cooling, making them ideal for many applications.
Disadvantages of Compression Refrigeration
Noise and Vibration
- Compression systems can be noisy and generate vibrations, which may not be suitable for some environments.
Use of Synthetic Refrigerants
- Many compression refrigeration systems use synthetic refrigerants, which can have negative environmental impacts.
Advantages of Absorption Refrigeration
Silent Operation
- Absorption systems operate quietly, making them ideal for noise-sensitive applications.
Use of Natural Refrigerants
- These systems typically use natural refrigerants, which can be more environmentally friendly.
Waste Heat Utilization
- Absorption refrigeration systems can utilize waste heat, making them energy-efficient in certain applications.
Disadvantages of Absorption Refrigeration
Lower Efficiency
- Absorption systems generally have lower COP values compared to compression systems.
Limited Capacity Range
- These systems may have a limited capacity range, making them less versatile for some applications.
Slower Cooling
- Absorption refrigeration systems typically cool spaces more slowly than compression systems.
Conclusion
Choosing the Right Refrigeration System
So, which refrigeration system is right for you? Here are some factors to consider:
Factors to Consider
Application
- Consider the specific cooling needs and requirements of your space.
Energy Source
- Think about the available energy sources and whether you can take advantage of waste heat for absorption systems.
Environmental Impact
- Consider the environmental implications of the refrigerants used and the system’s overall efficiency.
Budget
- Take into account the initial costs and ongoing energy expenses for each system.
In conclusion, understanding the fundamental differences between compression and absorption refrigeration can greatly inform your decision-making process as a homeowner. Both systems have their unique advantages and potential drawbacks, and your choice should be guided by your specific needs, environmental considerations, and budget constraints.
This guide has provided you with a starting point, but it’s always wise to consult with a professional in the field for personalized advice. Remember, the best cooling solution is one that aligns with your needs and promotes energy efficiency and sustainability. Always stay cool and informed!