“Discover the ins and outs of the diffusion absorption refrigeration system, its benefits, components, applications, and how it impacts the environment.”
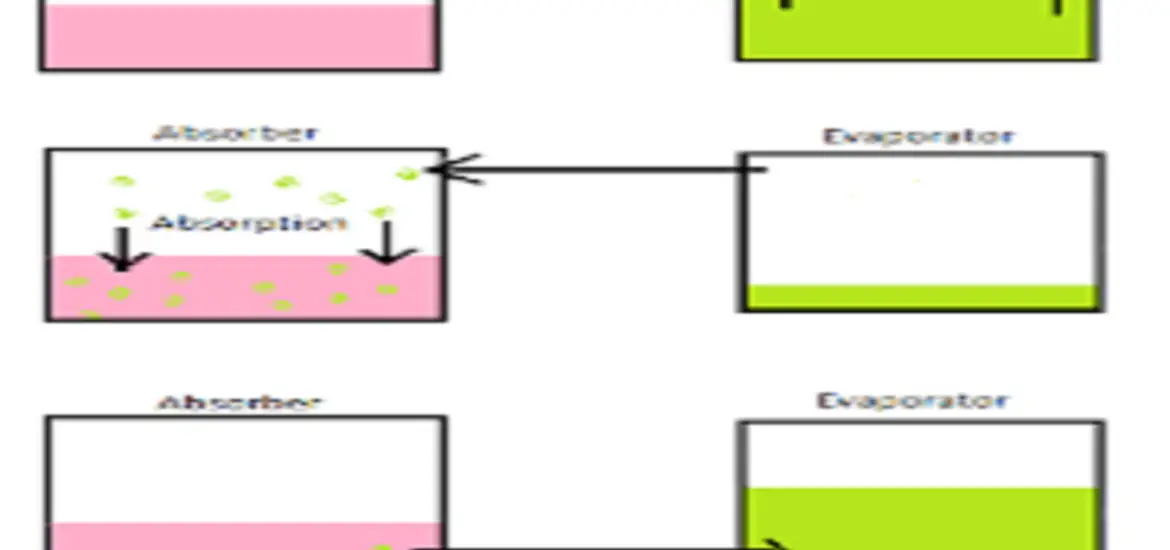
Table of Contents
Introduction to Diffusion Absorption Refrigeration System
Diffusion absorption refrigeration system (DARS) is taking the cooling world by storm. It’s green, efficient, and versatile. But what exactly is it? Let’s break it down, step by step.
Definition and working principle
A DARS is a type of cooling system that relies on heat energy to power the refrigeration process. This innovative technology combines absorption, diffusion, and evaporation processes to achieve cooling without the need for electricity or moving parts.
Key components
The magic happens thanks to four main components: generator, absorber, evaporator, and condenser. Together, they create an environment where the refrigerant and absorbent can interact and produce cooling effects.
Absorption, diffusion, and evaporation process
At the heart of the system, absorption and diffusion work hand-in-hand to separate the refrigerant from the absorbent. The evaporator then takes over, cooling the air or substance that needs to be chilled. Simple, right?
For more articles like this click here – – Absorption Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Understanding It
Advantages and disadvantages
Like everything in life, DARS has its pros and cons. Let’s weigh them up.
Energy efficiency
DARS is known for its energy efficiency. It uses heat sources like solar energy, waste heat, or even natural gas, making it an excellent alternative to conventional, electricity-hungry cooling systems. Can you imagine the savings on your energy bill?
Environmental impact
With climate change being a hot topic, DARS shines as an eco-friendly solution. It uses natural refrigerants and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Mother Nature would certainly give it a thumbs up!
Cost and maintenance
Although the initial investment might be higher, the long-term benefits of DARS are worth it. It requires minimal maintenance and has a longer lifespan than traditional cooling systems. Who wouldn’t want that?
Components of a Diffusion Absorption Refrigeration System
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s take a closer look at the components that make DARS tick.
Generator
Function
The generator is the starting point of the process. It heats up the refrigerant-absorbent solution, causing the refrigerant to vaporize and move to the next stage.
Construction
Typically, generators are made of metal and are designed to handle high temperatures and pressures. They’re built to last!
Heat sources
Generators can utilize various heat sources, such as solar energy, waste heat from industrial processes, or even natural gas. Talk about being resourceful!
Absorber
Function
The absorber is where the magic happens. It separates the refrigerant from the absorbent, allowing the refrigerant to move on to the evaporator.
Construction
Absorbers are often made of corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability and reliability. They’re designed to facilitate efficient heat and mass transfer between the refrigerant and absorbent.
Types of absorbers
There are various types of absorbers, including falling film, bubble, and spray absorbers. Each one has its own unique characteristics, but they all serve the same purpose: separating the refrigerant from the absorbent.
Evaporator
Function
The evaporator is the cool kid on the block. It’s where the refrigerant absorbs heat from its surroundings, causing it to evaporate and create a cooling effect.
Construction
Evaporators are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity, like copper or aluminum, to ensure efficient heat transfer.
Types of evaporators
There are different types of evaporators, such as plate, tube, and fin designs, each suited to specific applications and requirements.
Condenser
Function
The condenser plays a crucial role in the cooling process. It cools the refrigerant vapor, turning it back into a liquid that returns to the absorber, ready for another round.
Construction
Condensers are built with materials that can handle high pressures and temperatures, such as steel or copper.
Types of condensers
There are various types of condensers, including air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative designs. Each one has its unique features, but they all serve the same purpose: condensing the refrigerant vapor back into a liquid.
Refrigerant and absorbent
Function
The refrigerant and absorbent are the dynamic duo that makes the DARS work. The refrigerant absorbs heat and evaporates, while the absorbent helps separate the refrigerant from itself during the absorption process.
Common refrigerant-absorbent pairs
There are several refrigerant-absorbent pairs used in DARS, such as ammonia-water, water-lithium bromide, and water-lithium chloride. The choice depends on factors like temperature range, environmental impact, and system efficiency.
Selection criteria
Choosing the right refrigerant-absorbent pair is crucial. Factors to consider include safety, environmental impact, availability, and cost. It’s all about finding the perfect balance!
Thermodynamics of Diffusion Absorption Refrigeration System
Ready for a deep dive into the thermodynamics of DARS? Hold on tight!
Basic thermodynamic cycles
Absorption cycle
The absorption cycle involves the absorption of refrigerant vapor by the absorbent, creating a solution that moves to the generator.
Diffusion cycle
In the diffusion cycle, the refrigerant vapor diffuses through the absorbent, separating from it and moving on to the evaporator.
Evaporation cycle
During the evaporation cycle, the refrigerant absorbs heat and evaporates, producing the desired cooling effect.
Performance parameters
Coefficient of performance (COP)
The COP is a measure of how efficient a DARS is. The higher the COP, the more energy-efficient the system.
Capacity
Capacity refers to the amount of cooling a DARS can provide, typically measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units) or watts.
Energy efficiency ratio (EER)
EER is another way to measure the efficiency of a DARS. It’s the ratio of the cooling capacity to the power input. Just like with COP, a higher EER means a more efficient system.
Heat and mass transfer analysis
Heat transfer modes
Heat transfer in DARS occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. Understanding these modes is crucial for designing efficient and effective systems.
Mass transfer modes
Mass transfer in DARS occurs through diffusion and convection. A thorough analysis of mass transfer helps optimize the system’s performance.
Heat and mass transfer correlations
Correlations between heat and mass transfer help engineers design and analyze DARS for optimal performance and efficiency.
Applications of Diffusion Absorption Refrigeration System
DARS is versatile and can be used in various applications. Let’s explore some of them.
Domestic applications
Household refrigerators
DARS is perfect for household refrigerators, providing energy-efficient and eco-friendly cooling for your groceries.
Air conditioning systems
With its energy-saving and environmentally friendly features, DARS is an excellent choice for residential air conditioning systems.
Solar-powered cooling systems
By pairing DARS with solar panels, you can create a sustainable and cost-effective cooling solution for your home.
Industrial applications
Food processing and storage
DARS can be used in food processing and storage facilities, ensuring optimal temperature control while reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Chemical and pharmaceutical industries
Temperature-sensitive chemicals and pharmaceuticals can benefit from DARS’s precise temperature control and eco-friendly features.
Waste heat recovery systems
Industries that generate waste heat can use DARS to convert that heat into useful cooling, increasing overall efficiency and reducing waste.
Remote and off-grid applications
Rural electrification projects
DARS can bring cooling solutions to remote areas with limited or no access to electricity, improving the quality of life for those communities.
Telecommunication equipment cooling
Telecommunication towers and equipment in remote locations can use DARS for efficient and reliable cooling.
Military and emergency services
Portable DARS can provide cooling solutions for military and emergency services in remote or off-grid locations.
Recent Developments and Future Trends
As technology advances, so does DARS. Let’s explore the latest developments and trends shaping its future.
Technological advancements
Enhanced heat and mass transfer techniques
New techniques in heat and mass transfer are being developed to improve the efficiency and performance of DARS.
Advanced materials and coatings
Breakthroughs in materials and coatings are helping to increase the durability and efficiency of DARS components.
Improved component designs
Component designs are constantly evolving, leading to more efficient and compact DARS systems.
Market trends and growthThe DARS market is growing rapidly, driven by the demand for energy-efficient and eco-friendly cooling solutions. Let’s take a look at the trends shaping the industry.
Adoption of green technologies
As concerns about climate change and energy consumption rise, more businesses and consumers are turning to green technologies like DARS for their cooling needs.
Government policies and incentives
Government policies and incentives are promoting the adoption of DARS and other green technologies, further driving the growth of the market.
Global market analysis and projections
With increasing demand and favorable policies, the DARS market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, making it a promising sector for investment and development.
Future challenges and opportunities
While DARS has come a long way, there are still challenges to overcome and opportunities to seize. Let’s explore some of them.
Integration with renewable energy sources
Integrating DARS with renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can further enhance its eco-friendly credentials and increase its attractiveness to consumers and businesses.
Reducing costs and improving reliability
Continued research and development efforts are needed to reduce the costs and improve the reliability of DARS, making it more accessible and appealing to a wider audience.
Innovations in system controls and optimization
Advancements in system controls and optimization can help maximize the performance and efficiency of DARS, ensuring it remains a top choice for cooling applications in the future.