Evaporative vs refrigerated air conditioning – which one is right for you? As a homeowner, you know that staying cool and comfortable during those hot summer months is essential. But with so many options out there, it can be tough to decide which type of air conditioning system is the best fit for your home. In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between evaporative and refrigerated air conditioning, giving you the inside scoop on how each system works, the pros and cons, and how to choose the perfect system for your needs.
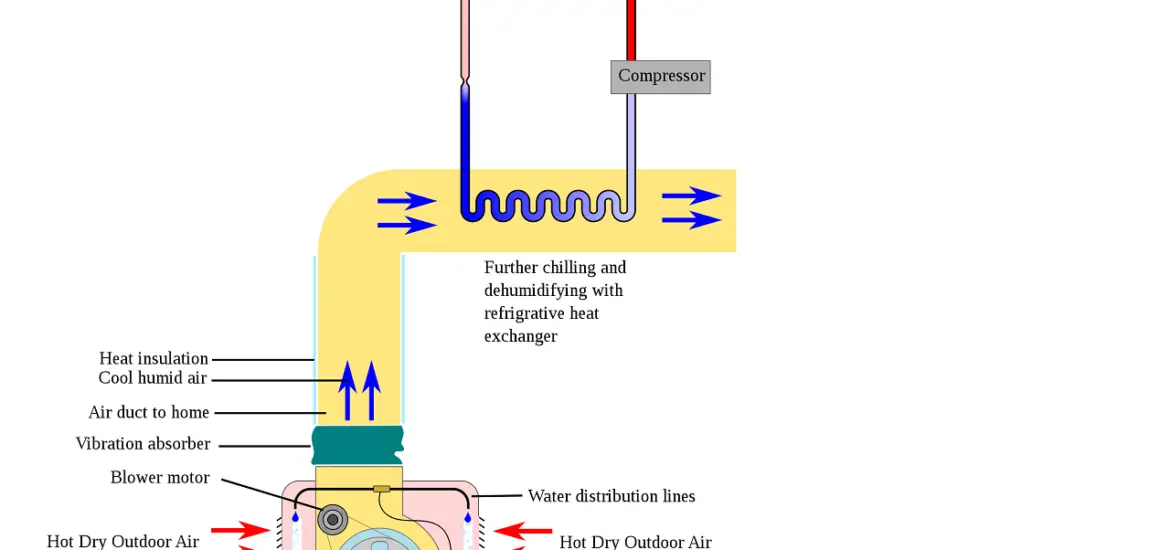
Table of Contents
Definition and Purpose of Air Conditioning
Maintaining Thermal Comfort
At its core, the purpose of air conditioning is to provide thermal comfort by maintaining a consistent, comfortable temperature inside your home. It helps us stay cool on those scorching hot days, ensuring we can relax and enjoy our living spaces without breaking a sweat.
Providing Clean, Fresh Air
But it’s not just about temperature – air conditioning systems also play a crucial role in filtering and circulating fresh air throughout our homes. This helps improve indoor air quality, reducing allergens and pollutants that can cause respiratory issues and other health problems.
Evaporative and Refrigerated Air Conditioning Systems
Overview of Evaporative Air Conditioning
Evaporative air conditioners, sometimes called swamp coolers, rely on the process of evaporation to cool the air. They’re popular in dry climates because they work best when the humidity is low. And guess what? They’re also eco-friendly and cost-effective! We’ll dive deeper into how they work and their pros and cons later in the article.
Overview of Refrigerated Air Conditioning
On the other hand, refrigerated air conditioners use a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle to remove heat and humidity from the air. These systems can be more effective in a variety of climates, including those with high humidity. But there’s a trade-off: they can be more expensive to install and run. Keep reading to find out all the details!
Click here: Vapor Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Keeping Things Chill, to read our other articles on vapor refrigeration.
Evaporative Air Conditioning Systems
Basic Principle of Evaporative Cooling
Evaporation and its Cooling Effect
Did you ever notice how you feel cooler when you step out of the pool on a hot day? That’s evaporative cooling in action! As the water on your skin evaporates, it absorbs heat, leaving you feeling cooler. Evaporative air conditioners use this same principle to cool the air inside your home.
How Evaporative Coolers Work
So how do evaporative coolers work their magic? Simple! They draw in hot, dry air and pass it through a wet pad. As the air flows over the pad, the water evaporates, cooling the air and adding moisture to it. This cooler, more humid air is then circulated throughout your home, providing a comfortable and refreshing indoor environment.
Advantages of Evaporative Air Conditioning
Energy Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness
One of the biggest benefits of evaporative air conditioners is their energy efficiency. Because they use the natural process of evaporation to cool the air, they consume far less electricity than refrigerated systems. This means lower energy bills for you and a smaller carbon footprint for the environment. How cool is that?
Fresh, Filtered Air
Evaporative coolers constantly bring in fresh air from the outside, which means they’re always circulating clean, filtered air throughout your home. Say goodbye to stale air and hello to a healthier living environment!
Environmental Benefits
Looking for an eco-friendly cooling solution? Evaporative coolers are a great choice. They don’t use harmful refrigerants, and their lower energy consumption means they produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Mother Earth will thank you!
Simple Installation and Maintenance
Another perk of evaporative air conditioners is their straightforward installation and maintenance. Most units are relatively easy to install, and their upkeep usually involves just cleaning or replacing the pads and occasionally checking the water supply. That means fewer headaches for you and more time to enjoy your cool, comfortable home.
Disadvantages of Evaporative Air Conditioning
Less Effective in High Humidity
While evaporative coolers work great in dry climates, their effectiveness drops in areas with high humidity. Since they add moisture to the air as they cool, they can struggle to provide adequate cooling when the air is already humid. So if you live in a humid region, a refrigerated system might be a better fit.
Limited Cooling Capacity
Evaporative air conditioners generally have a more limited cooling capacity compared to refrigerated systems. They can still provide significant relief on hot days, but they might not be able to achieve the same low temperatures as a refrigerated system, especially in very hot conditions.
Water Consumption
Although evaporative coolers are energy-efficient, they do consume water. In areas with water restrictions or where water conservation is a concern, this can be a drawback. However, they typically use less water than what’s required to generate electricity for refrigerated air conditioners.
Potential for Mold and Mildew
Because evaporative coolers add moisture to the air, there’s a risk of mold and mildew growth if the indoor humidity isn’t managed properly. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help mitigate this risk, but it’s something to be aware of.
Refrigerated Air Conditioning Systems
Basic Principle of Refrigerated Cooling
Vapor-compression Refrigeration Cycle
Refrigerated air conditioners work by using a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle. This involves a continuous process of compressing, condensing, expanding, and evaporating a refrigerant to absorb heat from the air and release it outside your home. Sounds pretty sci-fi, right?
How Refrigerated Air Conditioners Work
In a nutshell, a refrigerated air conditioner pulls warm air from your home and passes it over an evaporator coil filled with cold refrigerant. The refrigerant absorbs the heat from the air, cooling it down before it’s blown back into your home. Meanwhile, the now-warmed refrigerant is compressed and condensed, releasing its heat outside before the process starts all over again.
Advantages of Refrigerated Air Conditioning
Effective in Various Climates
One of the biggest selling points of refrigerated air conditioners is their effectiveness in a wide range of climates, including humid regions. They not only cool the air but also remove excess moisture, making them a great choice for those hot and sticky summer days.
Precise Temperature and Humidity Control
With a refrigerated air conditioning system, you have precise control over your indoor temperature and humidity levels. Most units come with programmable thermostats, allowing you to set your desired temperature and enjoy consistent comfort throughout your home.
Closed System for Cleaner Air
Refrigerated air conditioners operate in a closed system, which means they recirculate the air inside your home. This helps keep outdoor allergens and pollutants at bay, providing a cleaner indoor environment for you and your family.
Availability in Various Capacities and Configurations
Refrigerated air conditioners come in a variety of sizes and configurations, making it easy to find the perfect system for your home. Whether you need a small window unit for a single room or a central system to cool your entire house, there’s a refrigerated air conditioner to suit your needs.
Disadvantages of Refrigerated Air Conditioning
Higher Energy Consumption and Operating Costs
The main downside of refrigerated air conditioners is their higher energy consumption compared to evaporative coolers. This means higher electricity bills and a larger environmental impact. However, energy-efficient models and smart technologies can help offset some of these costs.
Environmental Concerns
Refrigerated air conditioners use refrigerants that can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if not properly handled. While newer models use more environmentally friendly refrigerants, it’s still important to properly maintain and dispose of these systems to minimize their impact on the environment.
More Complex Installation and Maintenance
Installing and maintaining a refrigerated air conditioning system can be more complex than an evaporative cooler. These systems often require professional installation, and their upkeep can be more involved, with regular filter changes and inspections needed to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Comparing Evaporative and Refrigerated Air Conditioning Systems
Climate Considerations
Evaporative Systems in Dry Climates
If you live in a dry climate, evaporative coolers can be an energy-efficient and cost-effective cooling solution. They work best when the humidity is low and can provide significant relief on hot, dry days.
Refrigerated Systems in Humid Climates
For those living in humid areas, refrigerated air conditioners may be the better choice. They’re designed to handle high humidity levels, removing excess moisture from the air while cooling your home effectively.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Evaporative Systems as a Cost-effective Solution
When it comes to energy efficiency and operating costs, evaporative coolers have the edge. Their lower energy consumption translates to lower electricity bills and a smaller environmental impact.
Refrigerated Systems and Energy-saving Technologies
While refrigerated air conditioners typically consume more energy, advances in technology have led to more energy-efficient models that can help offset some of these costs. Features like programmable thermostats, variable-speed fans, and smart controls can help you save on energy and maintain a comfortable home.
Environmental Impact
Greenhouse Gas emissions and Refrigerants
Both types of air conditioners have an environmental impact, but they differ in key ways. Evaporative coolers produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions due to their lower energy consumption and don’t use harmful refrigerants. Refrigerated systems, on the other hand, rely on refrigerants, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if not properly managed. However, newer models use more eco-friendly refrigerants to minimize their environmental impact.
Water Consumption in Evaporative Systems
While evaporative coolers have a smaller carbon footprint, they do consume water. In areas with water scarcity or restrictions, this can be a concern. However, it’s worth noting that the water used by evaporative coolers is usually less than the amount required to generate electricity for refrigerated systems.
Choosing the Right Air Conditioning System for Your Needs
Assessing your Specific Requirements
Climate and Location
When choosing between evaporative and refrigerated air conditioning, the climate and location of your home are important factors to consider. Dry climates favor evaporative coolers, while humid climates call for refrigerated systems.
Size and Layout of the Building
The size and layout of your home also play a role in determining the best cooling solution. You’ll need to consider the cooling capacity and configuration of the air conditioning system to ensure it can effectively cool your entire living space.
Budget Constraints and Long-term Operating Costs
Don’t forget to factor in the initial cost of the system and the long-term operating expenses. Evaporative coolers are generally more affordable upfront and have lower operating costs, while refrigerated systems can be more expensive to install and run but may offer greater comfort and flexibility.
Environmental Concerns
If environmental impact is a priority for you, consider the energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and water usage of each system. Evaporative coolers are generally more eco-friendly, but newer refrigerated systems with environmentally friendly refrigerants and energy-saving features can also be a responsible choice.
Professional Consultation and Installation
Importance of Proper Sizing and Design
Once you’ve decided on the right type of air conditioning system for your needs, it’s crucial to have it properly sized and designed for your home. An improperly sized system can lead to reduced efficiency, inadequate cooling, and higher energy costs.
Hiring Experienced Professionals
Consult with experienced professionals to help you choose and install the perfect air conditioning system. They can assess your home’s unique requirements, recommend the best system for your needs, and ensure it’s installed correctly for optimal performance and efficiency.
Conclusion
Summarizing the Differences Between Evaporative and Refrigerated Air Conditioning
In summary, evaporative and refrigerated air conditioning systems each have their own strengths and weaknesses. Evaporative coolers are energy-efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly, making them ideal for dry climates. Refrigerated systems, on the other hand, offer effective cooling and precise temperature control in a variety of climates, including humid areas.
Making an Informed Decision Based on Individual Needs and Circumstances
When it comes to choosing the right air conditioning system for your home, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. By carefully considering your specific needs, climate, budget, and environmental concerns, you can make an informed decision and enjoy a comfortable, cool home all summer long.