When you hear “refrigerant vapor pressure chart,” it might sound too technical. But as a homeowner, it’s useful to know about these charts and how they relate to your home’s HVAC system. In this article, we’ll simplify the concept for you, so you can see how this knowledge helps maintain a comfortable home and potentially save money in the long run.
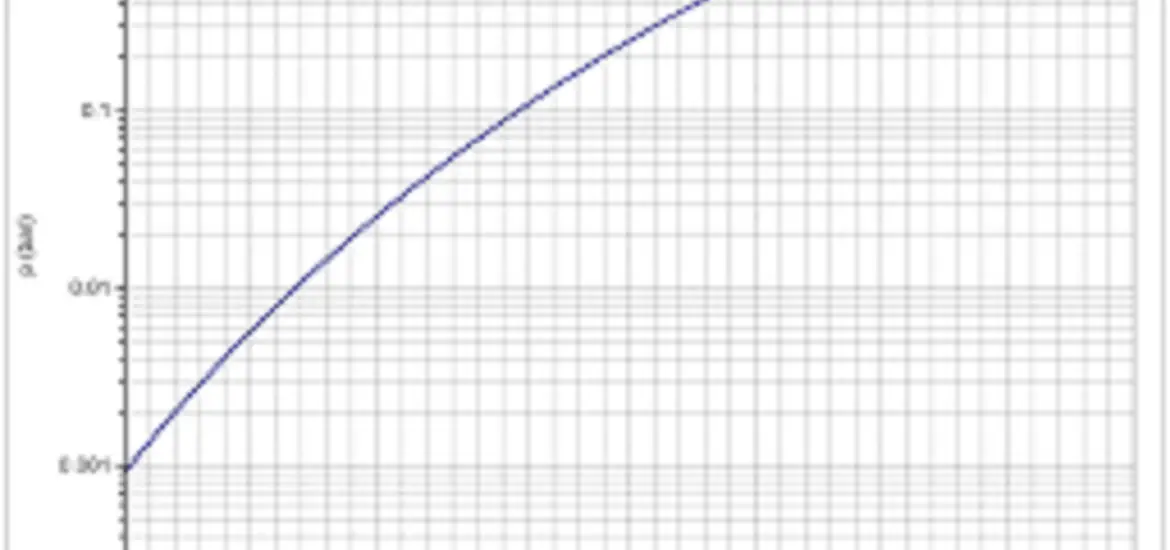
Table of Contents
Introduction to Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Chart
Understanding Refrigerant Vapor Pressure
Definition of Refrigerant Vapor Pressure
Starting with the basics: refrigerant vapor pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a refrigerant in its gaseous state. It’s a crucial aspect of how your HVAC system works to maintain a comfortable temperature throughout the year.
Factors Affecting Refrigerant Vapor Pressure
Temperature is the primary factor influencing refrigerant vapor pressure. As the temperature increases, so does the pressure. Other factors like the type of refrigerant, system design, and altitude also contribute.
Learn more about vapor pressure in this article – – Vapor Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Keeping Things Chill
Importance of Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Chart
HVAC System Design and Performance
Ever wondered why your HVAC system functions so effectively? It’s all thanks to the refrigerant vapor pressure chart! These charts help technicians design and optimize HVAC systems for maximum performance and efficiency.
Refrigerant Leak Detection and Maintenance
If your AC isn’t working as it should, a refrigerant leak might be the problem. By understanding refrigerant vapor pressure charts, you can detect and repair these leaks to keep your system operating smoothly.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Did you know that some refrigerants can harm the environment? Being aware of refrigerant vapor pressure charts can help you choose eco-friendly refrigerants for your HVAC system.
Types of Refrigerants
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
R-12 (Dichlorodifluoromethane)
R-12 was once a popular refrigerant, but it’s now phased out due to its harmful effects on the ozone layer. However, it’s still essential to be informed about it.
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs)
R-22 (Chlorodifluoromethane)
R-22 is another refrigerant that’s being phased out because of its environmental impact. It’s crucial to replace it with more eco-friendly alternatives in your HVAC system.
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
R-134a (Tetrafluoroethane)
R-134a is a widely-used refrigerant, especially in automotive air conditioning. It’s better for the environment than R-12 and R-22 but still has a high global warming potential.
R-410a (Azeotropic Mixture)
R-410a is an eco-friendlier refrigerant commonly used in residential and commercial HVAC systems. It has zero ozone depletion potential and lower global warming potential compared to R-22.
Natural Refrigerants
Ammonia (R-717)
Ammonia is an efficient and environmentally friendly refrigerant used in industrial refrigeration applications. However, it’s not typically used in residential HVAC systems due to its potential toxicity and flammability.
Carbon Dioxide (R-744)
Carbon dioxide, or R-744, is a natural refrigerant with a low global warming potential. It’s gaining popularity in commercial and industrial refrigeration, as well as some automotive air conditioning systems.
Hydrocarbons (R-600a, R-290)
Hydrocarbons like isobutane (R-600a) and propane (R-290) are eco-friendly refrigerants with low global warming potential. They’re becoming more common in household appliances and small commercial refrigeration systems.
Reading and Interpreting Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Charts
Basics of Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Charts
Pressure-Enthalpy (P-H) Diagrams
P-H diagrams are graphical representations of refrigerant properties, showing the relationship between pressure and enthalpy (heat content). They help technicians analyze and troubleshoot HVAC systems.
Temperature-Pressure (T-P) Charts
T-P charts display the relationship between temperature and pressure for a specific refrigerant. They’re essential for understanding how refrigerant pressure changes with temperature and for determining superheat and subcooling values.
How to Use Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Charts
Step-by-Step Guide for Reading Charts
Reading refrigerant vapor pressure charts may seem daunting, but with a little practice, you can do it! Start by locating the correct chart for your refrigerant, then follow the temperature and pressure values to understand your system’s performance.
Interpolation and Extrapolation Techniques
Sometimes, you’ll need to estimate values between data points on a chart (interpolation) or beyond the available data (extrapolation). These techniques help you make educated guesses about refrigerant properties when exact values aren’t provided.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Miscalculations and Misinterpretations
When working with refrigerant vapor pressure charts, it’s easy to make errors in calculations or misinterpret the data. Always double-check your work and consult a professional if you’re unsure.
Converting Between Different Units of Pressure and Temperature
Remember that different charts may use different units for pressure and temperature. Be careful when converting between units, and always use the appropriate conversion factors.
Applications of Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Charts
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
System Design
Refrigerant vapor pressure charts play a vital role in designing efficient and effective refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
By understanding these charts, you can troubleshoot problems with your HVAC system and perform necessary maintenance to keep it running smoothly.
Automotive HVAC Systems
Vehicle Climate Control
Refrigerant vapor pressure charts are also essential for maintaining and troubleshooting automotive climate control systems, ensuring a comfortable driving experience.
Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Thermal Management
As electric and hybrid vehicles become more popular, refrigerant vapor pressure charts play a crucial role in designing and maintaining efficient thermal management systems for these vehicles.
Industrial and Commercial Refrigeration
Food Storage and Processing
Proper refrigeration is vital for food storage and processing, and understanding refrigerant vapor pressure charts helps ensure that industrial and commercial refrigeration systems work effectively.
Cryogenic and Low-Temperature Applications
In applications requiring extremely low temperatures, such as cryogenics, refrigerant vapor pressure charts are invaluable for designing and maintaining the necessary refrigeration systems.
Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Chart Resources
Online Tools and Calculators
Web-Based Refrigerant Vapor Pressure Chart Applications
There are many web-based applications that provide refrigerant vapor pressure chart data, making it easy to access the information you need for your HVAC system.
Mobile Apps for HVAC Professionals
Several mobile apps offer refrigerant vapor pressure chart data and other HVAC tools, making it convenient for professionals to access the information on the go.
Books and Publications
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Handbooks
Many comprehensive handbooks on refrigeration and air conditioning include refrigerant vapor pressure chart data and other valuable information for homeowners and professionals alike.
Industry Standards and Guidelines
Industry standards and guidelines, such as those from ASHRAE and other organizations, provide essential information on refrigerant vapor pressure charts and proper HVAC system design and maintenance.
Training and Certification Programs
HVAC Technician Training Courses
HVAC technician training courses often cover refrigerant vapor pressure charts in depth, preparing professionals to use this knowledge in their daily work.
Refrigerant Handling and Safety Certification
Refrigerant handling and safety certification programs ensure that HVAC professionals have the necessary knowledge and skills to work with refrigerants and refrigerant vapor pressure charts safely and effectively.