Types of condenser are the central focus of this in-depth look at the heart of every cooling system. So, sit tight and get ready for a comprehensive breakdown!
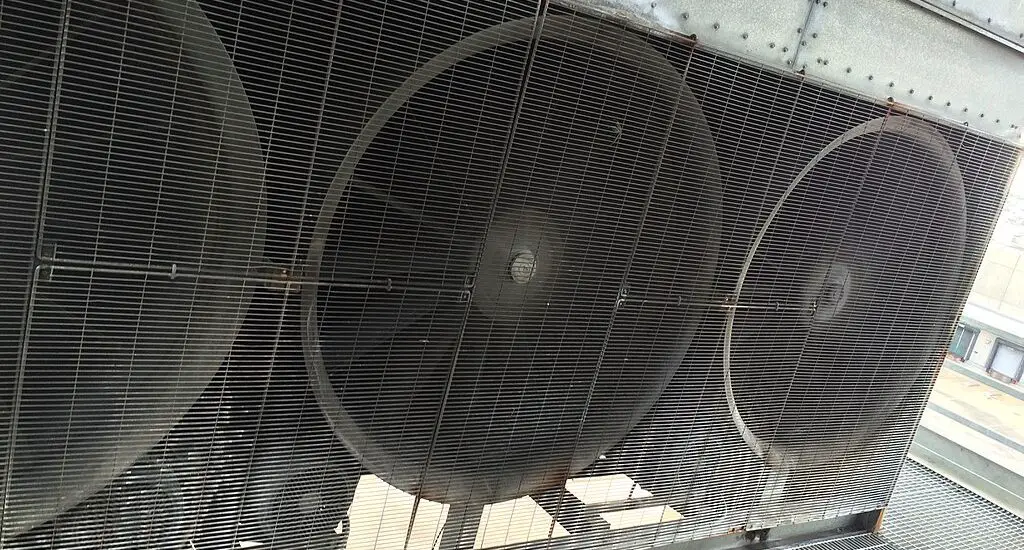
Table of Contents
Understanding the Types of Condenser
As we delve into the world of condensers, we find three primary players – air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condensers. Each type has unique attributes, offering distinct benefits and efficiencies depending on the application and environment.
Air-Cooled Condensers
Think of air-cooled condensers as the solitary hikers of the condenser world. These guys are typically used in smaller systems and work by transferring heat to the air directly around them. Their structure includes metal fins to increase surface area and enhance heat transfer.
Applications and Efficiency
So where do these lone rangers stride their stuff? Well, air-cooled condensers are usually found in residential and small commercial cooling systems. When it comes to efficiency, these condensers are more environment-dependent, and their performance is affected by air temperature and humidity.
Water-Cooled Condensers
Water-cooled condensers are like the team players of the condenser family. They function by transferring heat to water, which is then cooled by a cooling tower. It’s a little like passing the baton in a relay race – the condenser passes the heat to the water, which then gets cooled down.
Applications and Efficiency
You’ll usually find these team players in large commercial buildings where high cooling capacity is required. They might not be as commonly used as their air-cooled cousins, but they definitely score when it comes to efficiency, especially in warmer climates.
Evaporative Condensers
Finally, we’ve got evaporative condensers. If condensers were an orchestra, evaporative condensers would be the maestros conducting the whole show. They cleverly combine the roles of a cooling tower and a water-cooled condenser in one unit, effectively evaporating a portion of the cooling water to remove heat.
Applications and Efficiency
These maestros are often used in larger systems where space and water use are critical factors. Evaporative condensers offer superb efficiency, but they require regular maintenance to keep them at their peak performance.
Refrigerator Condenser Types
In the arena of refrigeration, two condenser types take center stage: static and dynamic condensers. Whether they’re quietly efficient or actively circulating air, these condensers are crucial in maintaining the chill factor in our fridges.
Static Condensers
Static condensers, common in older fridge models, are like the quiet librarians of the condenser world. They work silently, with no moving parts, and are usually attached to the back of the fridge where they quietly do their job.
Applications and Efficiency
You might think they’re a bit outdated, but these quiet librarians can be very efficient in the right conditions. They just need a little space for proper ventilation to do their job effectively.
Dynamic Condensers
Dynamic condensers, on the other hand, are the gym junkies of refrigerator condensers. They come with a fan, working hard to circulate air and improve the heat exchange process.
Applications and Efficiency
You’ll find these hard workers in newer fridge models, helping to keep your food cool and fresh. With proper care, they can provide excellent efficiency, but remember, they might need a bit more maintenance due to their moving parts.
Type of Condenser Used in Domestic Refrigerators
In our homes, dynamic condensers have become the mainstay, prized for their compact size and superior efficiency. Despite needing a bit more care, they’ve become an indispensable part of our everyday cooling needs.
Overview of Condensers in Domestic Refrigerators
So, what’s the go-to choice for our home fridges? Well, dynamic condensers are increasingly popular due to their high efficiency and compact size. They’re like the dependable friend you can always count on to keep your food cool and your energy bills low.
Advantages and Limitations
Like that dependable friend, dynamic condensers come with their own pros and cons. On the bright side, they’re efficient, and compact, and perform well even in tighter spaces. On the downside, they might need a bit more TLC with maintenance due to their moving parts.
Check out these other related articles…
Refrigerator Condenser Coils Not Hot: Reasons & 4 Sure Fixes
Refrigerator Condenser Fan Noise: 4 Easy Fixes
Refrigerator Condenser Fan Not Running: Fixed in 6 Easy Steps
Refrigerator Condenser Fan Air Direction: Your Easy Guide
How to Clean Commercial Refrigerator Condenser Coils
How to Clean Refrigerator Condenser Coils: A Simple Guide
Condenser Fan and Compressor Not Running: 8 Proven Solutions
Types of Condenser in Different Refrigeration Systems
Depending on the scale and requirements of refrigeration systems, different condensers emerge as the frontrunners. In commercial settings, water-cooled condensers hold sway, while in industrial systems, the power of evaporative condensers is harnessed for optimal cooling performance.
Types of Condenser in Commercial Refrigeration Systems
In the bustling world of commercial refrigeration, water-cooled condensers are often the top pick. Why? Because they’re great at handling high cooling capacities, making them ideal for large-scale operations where a lot of cooling is required. Just like the star player in a football match, they deliver when the stakes are high.
Types of Condenser in Industrial Refrigeration Systems
On the industrial front, it’s a different story. Evaporative condensers often take center stage due to their high efficiency and space-saving design. It’s like having a symphony orchestra deliver a powerful performance in a compact space. Who wouldn’t want that, right?
Choosing the Right Condenser
Choosing the right condenser isn’t about selecting the most powerful or the latest model; it’s all about finding the perfect fit for your specific cooling needs. Consider it like finding the perfect shoe; it should be the right size, provide adequate comfort, and suit the occasion. Similarly, the right condenser depends on the specific demands of your cooling system, whether it’s for a small residential unit, a large commercial building, or an industrial refrigeration system.
For instance, if you’re looking for a condenser for a small to medium-sized residential or commercial setup, air-cooled condensers might be a suitable choice. They’re generally easier to install, require less maintenance than other types, and work efficiently in cooler climates. However, if you live in an area with high ambient temperatures, an air-cooled condenser might struggle to maintain the desired temperature due to its dependence on the surrounding air for cooling.
On the other hand, if you have a large commercial building or an industrial setup that requires significant cooling capacity, you might want to consider a water-cooled condenser. They perform well in warmer climates and offer high efficiency, but they require a constant supply of water, which might be a limiting factor in areas with water scarcity.
Evaporative condensers can be a good choice if you want to combine the benefits of water-cooled and air-cooled condensers and if water and space conservation are important to you. They’re highly efficient and take up less space than a water-cooled condenser and cooling tower combination. However, they require regular maintenance to prevent scale buildup and to manage water quality.
In conclusion, when choosing a condenser, consider factors like the size and cooling demands of your system, local climate conditions, water availability, space constraints, and maintenance needs. A well-chosen condenser can provide effective cooling, energy savings, and a long, efficient lifespan for your system.