Working principle of evaporator in refrigeration system – ever wondered how that frosty fridge keeps your food fresh? It’s all thanks to the evaporator! This important component of the refrigeration world plays a vital role in keeping our food cold and our homes comfy. But what exactly is an evaporator, and how does it work? Keep reading to find out!
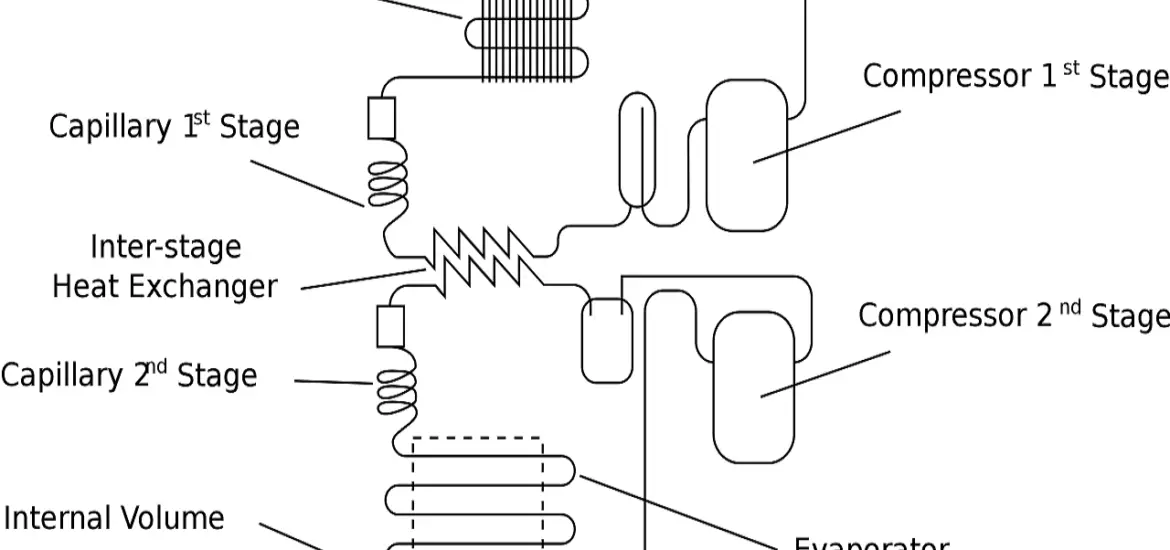
Table of Contents
Definition of Evaporator
An evaporator is a heat exchanger that’s responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding environment and evaporating the refrigerant. It’s the key component in the refrigeration cycle that provides the cooling effect.
Role of Evaporator in Refrigeration
Ever noticed how cold it feels when you’re sweating on a hot day? That’s because your sweat is evaporating, taking heat away from your body. The evaporator works in a similar way, absorbing heat from the air or other substances and using it to evaporate the refrigerant. This process cools the surrounding area, keeping your food fresh and your home cozy.
Types of Evaporators
There are various types of evaporators, including natural convection, forced convection, and direct expansion evaporators. Each type has its unique design and application, but they all work on the same basic principle.
Importance of Evaporator in Refrigeration System
Without the evaporator, there would be no cooling effect in the refrigeration system. It’s the evaporator that makes it possible to keep our food fresh, preserve medical supplies, and maintain comfortable temperatures in our homes and offices. Imagine life without refrigeration – not a pleasant thought, is it?
Read our other articles on evaporators in refrigeration – Evaporators in Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Understanding Your Fridge’s Unsung Hero
Working Principle of Evaporator in Refrigeration System
Basic Components of Refrigeration System
Before diving into the evaporator’s working principle, let’s take a quick look at the four main components of a refrigeration system:
Compressor
The compressor’s job is to pump the refrigerant throughout the system. It compresses the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure.
Condenser
The condenser is another heat exchanger that releases the heat absorbed by the evaporator. It cools the hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas, turning it back into a liquid.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It reduces the pressure and temperature of the liquid refrigerant, preparing it for the evaporation process.
Evaporator
And finally, the star of the show: the evaporator! This is where the magic happens, as the refrigerant absorbs heat and evaporates, cooling the surrounding area.
Understanding the Evaporator Working Principle
Heat Exchange Process
The evaporator’s main function is to absorb heat from its surroundings. It does this by exchanging heat between the refrigerant and the air or substance being cooled. The refrigerant absorbs the heat, causing it to evaporate and change from a low-pressure liquid to a low-pressure gas. This process is called the heat exchange process, and it’s the heart of the evaporator’s working principle.
Refrigerant Flow in Evaporator
As the refrigerant flows through the evaporator, it absorbs heat and evaporates. The now gaseous refrigerant moves along the evaporator coils, eventually reaching the outlet. From there, it’s sucked back into the compressor, where the cycle begins again. It’s a continuous loop of cooling and heat transfer that keeps your fridge frosty and your home comfy.
Cooling and Refrigeration Effect
So, how does all this heat transfer and evaporation lead to cooling? As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it evaporates, taking the heat with it. This cools the air or substance in contact with the evaporator. And voila! You’ve got yourself a refrigeration effect.
Factors Affecting Evaporator Efficiency
Temperature Difference
The greater the temperature difference between the refrigerant and the air or substance being cooled, the more efficient the evaporator will be. A higher temperature difference means more heat transfer, leading to better cooling performance.
Refrigerant Properties
The type of refrigerant used can also affect the evaporator’s efficiency. Some refrigerants have better heat absorption properties than others, making them more effective at cooling. It’s essential to choose the right refrigerant for your specific application.
Evaporator Surface Area
Another factor that impacts evaporator efficiency is the surface area. A larger surface area allows for more heat exchange, leading to improved cooling performance. That’s why you’ll often see evaporators with fins or other heat exchange-enhancing features.
Types of Evaporators in Refrigeration Systems
Natural Convection Evaporators
Plate Type Evaporators
These evaporators consist of flat plates that absorb heat from the air or substance being cooled. They rely on natural convection for heat transfer, with the cold refrigerant flowing through the plates, absorbing heat and evaporating.
Roll Bond Evaporators
Roll bond evaporators are made from two aluminum sheets that are bonded together and filled with refrigerant. The refrigerant flows through the channels between the sheets, absorbing heat and evaporating. They’re commonly used in refrigerators and freezers.
Fin and Tube Evaporators
Fin and tube evaporators consist of tubes containing refrigerant surrounded by fins. The fins increase the surface area for heat transfer, making these evaporators more efficient. They’re often used in air conditioning systems.
Forced Convection Evaporators
Shell and Tube Evaporators
These evaporators consist of a shell containing a series of tubes. The refrigerant flows through the tubes, while the substance being cooled (usually a liquid) flows around the tubes. A pump or fan is used to force the liquid through the shell, enhancing heat transfer.
Shell and Coil Evaporators
Shell and coil evaporators are similar to shell and tube evaporators, but they feature a coiled tube design inside the shell. This design increases the surface area for heat transfer and improves efficiency. They’re commonly used in various applications, including air conditioning and industrial refrigeration.
Plate Heat Exchanger Evaporators
Plate heat exchanger evaporators consist of a series of stacked plates with channels for the refrigerant and the substance being cooled. Forced convection is used to enhance heat transfer, making these evaporators highly efficient. They’re often used in commercial and industrial refrigeration systems.
Direct Expansion and Flooded Evaporators
Differences and Applications
Direct expansion evaporators use a controlled flow of refrigerant to provide cooling, while flooded evaporators have a pool of refrigerant covering the evaporator tubes. Direct expansion evaporators are more commonly used in residential and commercial applications, while flooded evaporators are often found in industrial settings where large-scale cooling is required.
Applications of Evaporators in Refrigeration Systems
Domestic Refrigeration
Refrigerators and Freezers
Evaporators are essential components in household refrigerators and freezers, providing the cooling effect that keeps our food fresh and safe to eat. They work tirelessly behind the scenes to maintain the perfect temperature for food storage.
Air Conditioners
Air conditioning systems also rely on evaporators to keep our homes and offices comfortable. The evaporator absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it before it’s circulated back into the room. Without evaporators, we’d be left to sweat it out during those hot summer months!
Commercial Refrigeration
Supermarkets and Grocery Stores
Ever walked into a supermarket and felt that refreshing blast of cold air? That’s thanks to the evaporators working hard in the refrigeration systems. They keep the shelves stocked with fresh produce, dairy products, and frozen goods, making our shopping experience a breeze.
Cold Storage Facilities
Cold storage facilities depend on evaporators to maintain the low temperatures required for preserving perishable goods. These facilities store everything from fresh fruits and vegetables to pharmaceutical products, ensuring they stay in optimal condition until they reach their final destination.
Industrial Refrigeration
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
Evaporators play a crucial role in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, where precise temperature control is required for manufacturing processes and product storage. From chemical reactions to drug formulation, evaporators help maintain the perfect conditions for success.
Food Processing Industries
In the food processing industry, evaporators are used to control temperature during various stages of production, including cooking, cooling, and freezing. They help ensure that the final products are safe, fresh, and delicious.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Evaporators in Refrigeration Systems
Common Issues with Evaporators
Ice Build-up
Ice build-up on the evaporator coils can reduce cooling efficiency and lead to higher energy consumption. Regular defrosting and maintenance can help prevent this issue.
Reduced Cooling Efficiency
Over time, evaporators can become less efficient due to dirt, dust, or debris buildup on the coils. This can cause reduced cooling performance and increased energy consumption. Regular cleaning and maintenance can help keep your evaporator running at peak efficiency.
Refrigerant Leaks
Leaks in the refrigerant lines or connections can lead to decreased performance and potential damage to the environment. It’s essential to regularly inspect your refrigeration system for leaks and address any issues promptly.
Maintenance Tips for Evaporators
Regular Cleaning
Keeping your evaporator coils clean is crucial for maintaining optimal cooling efficiency. Use a soft brush or vacuum cleaner to remove dust and debris from the coils, and consider using a coil cleaner for more stubborn grime.
Checking for Refrigerant Leaks
Regularly inspect your refrigeration system for signs of refrigerant leaks, such as oily residue around connections or hissing sounds. If you suspect a leak, contact a professional technician to assess and repair the issue.
Inspecting Insulation
Check the insulation around your evaporator and refrigeration lines for signs of wear or damage. Proper insulation helps maintain efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
Troubleshooting Evaporator Issues
Diagnosing Common Problems
If you’re experiencing issues with your evaporator, start by checking for obvious signs of problems, such as ice buildup, dirty coils, or refrigerant leaks. Consult your system’s manual for guidance on diagnosing and resolving common issues.
Resolving Evaporator Issues
For minor issues, such as dirty coils or ice buildup, you may be able to resolve the problem yourself through cleaning and maintenance. For more complex problems or refrigerant leaks, it’s best to contact a professional technician for assistance.
Conclusion
Importance of Understanding Evaporator Working Principle
Understanding the working principle of evaporator in refrigeration systems is essential for anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of these systems. A solid grasp of evaporator fundamentals will help you make informed decisions and ensure the optimal performance of your refrigeration system.
Future Developments and Innovations in Evaporator Technology
As technology advances, we can expect to see even more efficient and environmentally friendly evaporator designs in the future. Innovations in materials, manufacturing techniques, and control systems will continue to push the boundaries of evaporator performance, helping us stay cool and comfortable in an ever-changing world.