Have you ever heard about absorption chiller types and how they can revolutionize the way we cool our buildings? You’re not alone! Absorption chillers have become increasingly popular due to their energy-efficient nature and ability to reduce our carbon footprint. So, let’s dive right into the world of absorption chillers and explore their fascinating features.
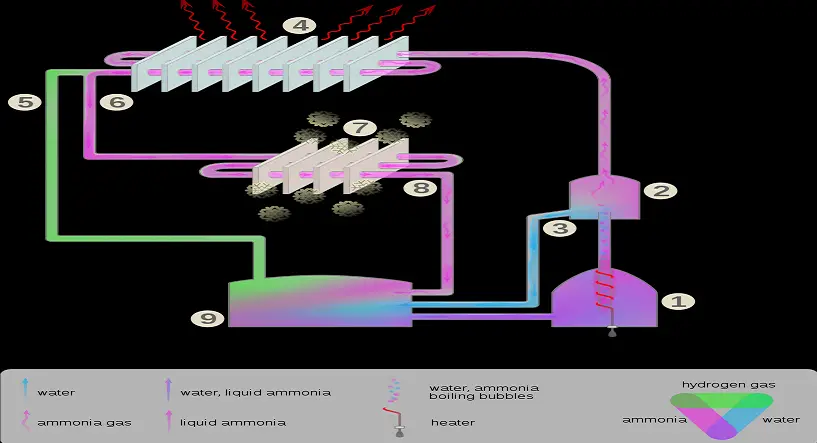
Table of Contents
Definition of Absorption Chiller Types
Absorption chillers are cooling systems that use heat sources instead of electricity to generate cool air. They’re different from traditional chillers in that they rely on a chemical process involving heat and refrigerants. Cool, right?
Components of Absorption Chillers
These chillers consist of four main components: the evaporator, absorber, generator, and condenser. Each part plays a crucial role in creating that refreshing cool air we crave during those hot summer months.
Working Principle of Absorption Chillers
How do absorption chillers work, you ask? It’s all about chemistry! Heat is applied to a refrigerant and absorbent mixture, causing the refrigerant to evaporate while the absorbent separates. The refrigerant vapor then condenses, releasing cool air. Genius!
Types of Absorption Chillers
Now, let’s talk about the various absorption chiller types available. They come in several flavors: single-effect, double-effect, triple-effect, direct-fired, and indirect-fired chillers. Each has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, so let’s take a closer look.
Single-Effect Absorption Chillers
These are the simplest chillers, using one heat source and one evaporation process. They’re cost-effective but less efficient than other types.
Double-Effect Absorption Chillers
As the name suggests, double-effect chillers use two heat sources and two evaporation processes, resulting in higher efficiency and better performance. Sounds impressive, right?
Triple-Effect Absorption Chillers
Triple-effect chillers take it up a notch with three heat sources and evaporation processes. They’re the most efficient but also the most complex and expensive.
Direct-fired Absorption Chillers
These chillers use a direct flame to heat the refrigerant, which is highly efficient but may produce harmful emissions. Weighing the pros and cons is key with this type.
Indirect-fired Absorption Chillers
Indirect-fired chillers, on the other hand, use a heat exchanger to heat the refrigerant. This results in fewer emissions but may be less efficient than direct-fired chillers.
Single-Effect Absorption Chillers
Overview of Single-Effect Chillers
Single-effect chillers are the most common type, known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They’re perfect for small-scale applications where high efficiency isn’t a top priority.
Working Mechanism
Their working mechanism is straightforward: one heat source causes the refrigerant to evaporate, resulting in cool air. Easy peasy, right?
Advantages and Disadvantages
While single-effect chillers are cost-effective and easy to maintain, their efficiency is lower than other types, which may be a deal-breaker for some. So, it’s all about finding the right balance for your needs.
Applications of Single-Effect Chillers
These chillers are versatile and can be used in various settings. Let’s take a look at some examples.
Commercial Uses
Single-effect chillers are great for smaller commercial spaces like retail stores, restaurants, and small office buildings. They provide adequate cooling without breaking the bank.
Industrial Uses
In the industrial sector, single-effect chillers are ideal for applications where high-efficiency cooling isn’t crucial, like warehouses and certain manufacturing processes.
For more in-depth articles on absorptions, click here: Absorption Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Understanding It
Double-Effect Absorption Chillers
Overview of Double-Effect Chillers
Double-effect chillers are the next step up in efficiency and performance. They use two heat sources and evaporation processes to provide better cooling, but at a higher price.
Working Mechanism
These chillers have a more complex mechanism, using two separate heat sources to evaporate the refrigerant, ultimately leading to more efficient cooling. Sounds like a win-win!
Advantages and Disadvantages
Double-effect chillers offer higher efficiency and better performance than single-effect chillers, but they also come with a heftier price tag and require more maintenance. Is it worth the trade-off? That’s up to you!
Applications of Double-Effect Chillers
These chillers are perfect for large-scale commercial and industrial applications where high efficiency is a must. Let’s explore some examples.
Commercial Uses
Large office buildings, hotels, and healthcare facilities can benefit from the enhanced efficiency of double-effect chillers, providing optimal comfort for occupants.
Industrial Uses
In industries like food processing, chemical production, and manufacturing, double-effect chillers can help maintain precise temperature control, ensuring product quality and safety.
Triple-Effect Absorption Chillers
Overview of Triple-Effect Chillers
Triple-effect chillers are the cream of the crop in terms of efficiency, using three heat sources and evaporation processes. They’re the most advanced and expensive option, but they deliver unparalleled performance.
Working Mechanism
The working mechanism of triple-effect chillers is similar to that of double-effect chillers, but with an additional heat source and evaporation process. This results in even more efficient cooling. Can you believe it?
Advantages and Disadvantages
While triple-effect chillers boast the highest efficiency, they also have the highest upfront and maintenance costs. So, you’ll need to carefully consider whether the benefits outweigh the costs for your specific application.
Applications of Triple-Effect Chillers
Triple-effect chillers are suitable for large-scale applications where efficiency and performance are of utmost importance. Here are some examples:
Commercial Uses
Large hotels, resorts, and data centers can benefit from the enhanced efficiency and performance of triple-effect chillers, ensuring a comfortable environment and protecting valuable equipment.
Industrial Uses
Triple-effect chillers are ideal for demanding industrial applications, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, where precise temperature control is critical for product quality and safety.
Direct-Fired Absorption Chillers
Overview of Direct-Fired Chillers
Direct-fired absorption chillers are a unique type that uses a direct flame to heat the refrigerant. They’re highly efficient but come with some potential drawbacks, like emissions concerns. Let’s dive deeper!
Working Mechanism
These chillers use a burner to produce a flame that directly heats the refrigerant. This high-temperature heat source leads to a more efficient evaporation process. It’s like turning up the heat in the kitchen!
Advantages and Disadvantages
Direct-fired chillers have excellent efficiency and performance, but their downside is the potential for harmful emissions due to the combustion process. Weighing the pros and cons is essential when considering this option.
Applications of Direct-Fired Chillers
These chillers can be used in various commercial and industrial settings where high efficiency is desirable, and emissions can be managed. Let’s check out some examples.
Commercial Uses
Large-scale commercial spaces like shopping malls and conference centers can benefit from the superior efficiency of direct-fired chillers, as long as emissions are adequately controlled.
Industrial Uses
Direct-fired chillers can be used in industries like power generation and waste-to-energy plants, where high-efficiency cooling is necessary, and emissions can be managed effectively.
Indirect-Fired Absorption Chillers
Overview of Indirect-Fired Chillers
Indirect-fired absorption chillers use a heat exchanger to heat the refrigerant instead of a direct flame, resulting in fewer emissions but potentially lower efficiency. Let’s explore this interesting alternative!
Working Mechanism
Indirect-fired chillers use a heat exchanger to transfer heat from an external source to the refrigerant, avoiding direct combustion. It’s like warming up by the fire without getting too close!
Advantages and Disadvantages
These chillers have the advantage of producing fewer emissions compared to direct-fired chillers, but they may be slightly less efficient due to the indirect heating process. It’s all about finding the right balance for your needs.
Applications of Indirect-Fired Chillers
Indirect-fired chillers can be used in various commercial and industrial applications where emissions are a concern. Let’s take a look at some common uses.
Commercial Uses
Commercial buildings like schools, museums, and theaters can benefit from the lower emissions provided by indirect-fired chillers while still enjoying efficient cooling.
Industrial Uses
Industries with strict emissions regulations, such as food and beverage production or pharmaceutical manufacturing, can take advantage of the lower emissions associated with indirect-fired chillers.
Absorption Chiller Uses
Commercial Applications
Office Buildings
Absorption chillers can provide energy-efficient cooling for office buildings, ensuring a comfortable environment for employees and clients alike.
Hotels and Resorts
Hotels and resorts can use absorption chillers to maintain comfortable temperatures for guests while reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities
Absorption chillers can help hospitals and healthcare facilities maintain a comfortable and sterile environment, ensuring patient comfort and safety while also reducing energy consumption.
Industrial Applications
Food Processing
In the food processing industry, absorption chillers can provide precise temperature control to ensure food safety and quality, all while reducing energy costs.
Chemical Industry
Absorption chillers can be utilized in the chemical industry to maintain strict temperature controls for sensitive processes, ensuring product quality and safety while minimizing energy consumption.
Manufacturing Facilities
Manufacturing facilities can use absorption chillers to maintain optimal temperatures for equipment and processes, improving efficiency and reducing energy costs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Absorption Chiller
Efficiency and Performance
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
When selecting an absorption chiller, consider its COP, which measures the ratio of cooling output to the input energy. A higher COP indicates better efficiency and performance.
Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER)
EER is another metric to consider, as it measures the cooling output per unit of energy input. A higher EER signifies better energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Consider the greenhouse gas emissions associated with different absorption chiller types, as this can impact the environment and potentially lead to regulatory issues.
Ozone Depletion Potential
Choose a chiller with a low ozone depletion potential to minimize its impact on the ozone layer and support environmental sustainability.
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment
Factor in the upfront cost of the chiller, as this will affect your budget and return on investment. Higher efficiency chillers may have higher initial costs but can result in long-term savings.
Operating and Maintenance Costs
Consider the ongoing operating and maintenance costs associated with the chiller, as these can impact the overall cost-effectiveness of the system.
Space Requirements
Chiller Size and Footprint
Take into account the size and footprint of the chiller, ensuring it can fit within your available space and meet your cooling needs.
Noise Levels and Vibration
Consider the noise levels and vibration produced by the chiller, as these factors can impact the comfort of building occupants and the overall user experience.
Conclusion
Summary of Absorption Chiller Types and Uses
In summary, absorption chillers come in various types, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. From single-effect to triple-effect, and direct-fired to indirect-fired, there’s an absorption chiller to meet every need and budget. By considering factors like efficiency, performance, environmental impact, and cost, you can choose the perfect absorption chiller for your specific application.
Future Trends in Absorption Chillers
Technological Advancements
As technology advances, we can expect to see even more efficient and environmentally friendly absorption chillers hitting the market, providing even greater benefits for users.
Increasing Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
With a growing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability, absorption chillers are poised to play an increasingly important role in our efforts to combat climate change and reduce our overall energy consumption. So, get ready for a greener and more energy-efficient future with these innovative cooling solutions!