Absorption fridge power consumption is a hot topic these days, especially when it comes to energy efficiency and environmental impact. So, what exactly is an absorption fridge, and how does it compare to the conventional compressor fridge? Let’s explore this fascinating world of cooling technology and find out how to make the best use of it.
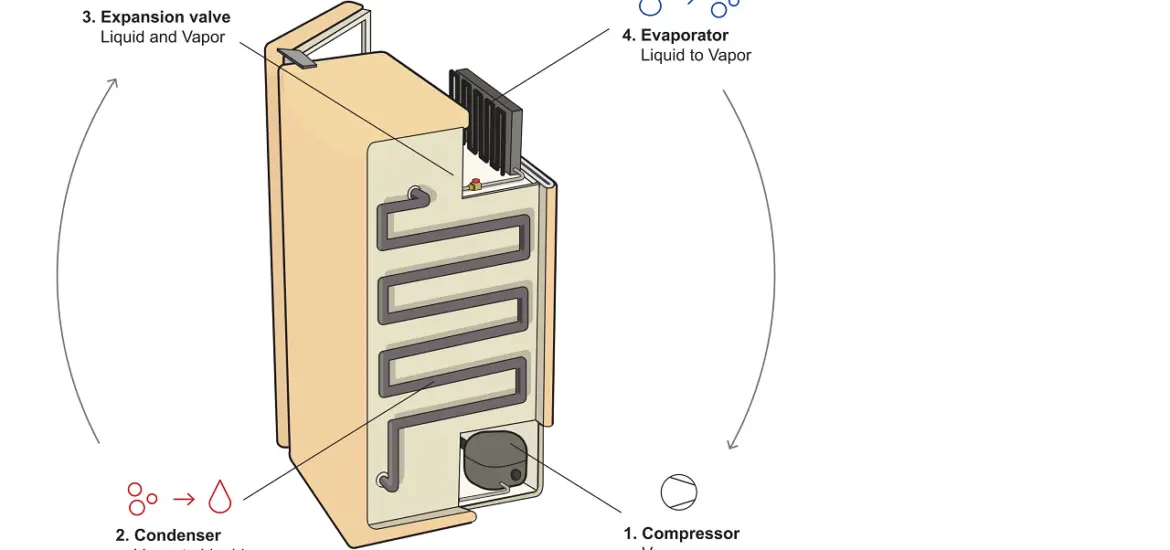
Table of Contents
Definition of Absorption Fridge
An absorption fridge is a type of refrigerator that uses a heat-driven process instead of a mechanical compressor to cool its contents. This unique design makes it quieter and more energy-efficient in certain situations compared to traditional fridges.
Comparison with Conventional Compressor Fridges
While compressor fridges use an electric motor to compress refrigerant, absorption fridges rely on heat to drive the cooling cycle. This difference in operation makes absorption fridges a great option for off-grid living or areas with limited electricity access. However, they might not be as energy-efficient as conventional fridges in some cases.
Key Components of an Absorption Fridge
An absorption fridge consists of three main components: the evaporator, the absorber, and the generator. Together, these parts work in harmony to create a cooling effect without the need for mechanical parts, which leads to quieter operation.
Absorption Fridge Power Consumption
Working Principle
The Absorption Cooling Cycle
At the heart of the absorption fridge is the absorption cooling cycle. It involves a series of chemical reactions between the refrigerant (usually ammonia) and an absorbent (usually water) to create a cooling effect. Who knew that mixing chemicals could keep our food fresh, right?
Role of Heat in the Process
Heat plays a crucial role in driving the absorption cooling cycle. It’s used to separate the refrigerant from the absorbent, allowing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the fridge’s interior. Sounds counterintuitive, but it’s a simple and effective way to generate cold temperatures.
Factors Affecting Power Consumption
Size of the Fridge
It’s no secret that larger fridges consume more power, but did you know that the size of an absorption fridge can significantly impact its efficiency? Bigger isn’t always better, so choose wisely.
Ambient Temperature
Surrounding temperatures have a considerable effect on absorption fridge power consumption. High ambient temperatures can force the fridge to work harder, causing it to consume more energy. So, try to keep your fridge in a cool spot.
Fridge Temperature Settings
Setting your fridge to a lower temperature might keep your food colder, but it can also lead to higher power consumption. Striking a balance between energy efficiency and food safety is essential.
Insulation Quality
Good insulation is vital for any fridge, and absorption fridges are no exception. High-quality insulation helps maintain cold temperatures, reducing the energy needed to keep things cool.
Frequency of Door Opening
Constantly opening the fridge door lets out cold air, forcing the fridge to consume more energy to maintain the desired temperature. So, remember to keep those fridge raids to a minimum!
Energy Sources for Absorption Fridges
Gas
Gas-powered absorption fridges are quite popular, especially in off-grid situations. They use propane or natural gas as a heat source, making them an excellent option for those without reliable access to electricity.
Electricity
Electric absorption fridges use electrical heating elements to generate the heat needed for the absorption cooling cycle. These models are a good fit for homes with a stable electrical supply.
Solar Power
For the eco-conscious, solar-powered absorption fridges are an attractive choice. They use solar energy to provide the heat required for the cooling process, making them a sustainable and environmentally friendly option.
Read our other articles on absorption refrigeration – Absorption Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Understanding It
Power Consumption Comparison with Conventional Fridges
Efficiency Differences
When it comes to energy efficiency, absorption fridges might not always outperform conventional fridges. Factors like size, temperature settings, and insulation quality can influence their performance. However, in specific situations like off-grid living, absorption fridges can be the more energy-efficient choice.
Use Cases and Suitability
While absorption fridges may not be suitable for every household, they excel in specific situations like RVs, boats, remote locations, and off-grid living. Consider your unique needs and energy requirements before making a decision.
Improving the Efficiency of Absorption Fridges
Selecting the Right Fridge Size
Choosing the appropriate fridge size can help optimize energy consumption. Smaller fridges typically use less power, so consider your storage needs and select a fridge that meets them without going overboard.
Proper Insulation
Ensuring your fridge is well-insulated can reduce energy consumption and improve overall efficiency. Invest in a high-quality model with good insulation, and keep it away from direct sunlight or heat sources.
Optimal Temperature Settings
Setting your fridge to the optimal temperature range (typically between 35-38°F or 2-3°C) can help balance energy efficiency and food safety. Resist the temptation to crank it colder than necessary!
Regular Maintenance
A well-maintained fridge runs more efficiently, so make sure to clean the cooling coils, check the door seals, and perform any other necessary maintenance tasks on a regular basis.
Reducing Door Opening Frequency
Limiting the number of times you open the fridge door can help conserve energy. Plan your meals in advance and try to gather all the ingredients you need in one go to minimize energy waste.
Environmental Impact of Absorption Fridges
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Gas-Powered Fridges
Gas-powered absorption fridges produce greenhouse gas emissions when burning propane or natural gas. However, these emissions can be relatively low compared to other appliances, especially if the fridge is well-maintained and operated efficiently.
Electric and Solar-Powered Fridges
Electric and solar-powered absorption fridges have a lower environmental impact, as they do not produce direct greenhouse gas emissions. Their carbon footprint depends on the source of the electricity used, so opt for renewable energy sources whenever possible.
Refrigerants and Environmental Concerns Ammonia
Ammonia, commonly used as a refrigerant in absorption fridges, is a natural substance that doesn’t contribute to ozone depletion or global warming. However, ammonia can be toxic in high concentrations, so proper handling and maintenance are crucial to ensure safety.
Water
Water is another refrigerant used in some absorption fridges. It’s an environmentally friendly option with no harmful effects on the ozone layer or global warming. However, water-based refrigeration systems may not be as efficient as those using ammonia.
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
Some absorption fridges use HFCs as refrigerants, which can contribute to global warming. While HFCs are being phased out in many countries, it’s essential to consider the environmental impact of your chosen fridge before purchasing.
Energy Efficiency and Carbon Footprint
The energy efficiency of absorption fridges varies depending on factors like size, insulation quality, and temperature settings. By choosing an appropriately sized fridge and optimizing its operation, you can minimize its carbon footprint and help protect the environment.
Applications of Absorption Fridges
Residential Use
While not as common as conventional fridges, absorption fridges can be used in residential settings where quiet operation, off-grid capability, or unique energy requirements are a priority.
Commercial and Industrial Use
Absorption fridges are popular in commercial and industrial settings like hotels, restaurants, and laboratories. Their quiet operation, reliability, and adaptability make them a great choice for these environments.
Recreational Vehicles and Off-Grid Living
For those living off the grid or enjoying the nomadic lifestyle in an RV, absorption fridges can be a game-changer. Their ability to run on various energy sources, including propane, solar power, or electricity, makes them perfect for life on the move.
Remote Locations and Developing Countries
In remote areas or developing countries with limited access to electricity, absorption fridges can be a lifesaver. Their ability to operate using alternative energy sources, like gas or solar power, makes them ideal for these situations.
Conclusion
Pros and Cons of Absorption Fridges
Absorption fridges come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. While they offer quiet operation, adaptability, and off-grid capabilities, they may not be as energy-efficient as conventional fridges in some cases. Weighing the pros and cons is crucial in determining if an absorption fridge is right for you.
Future Developments and Innovations in Absorption Refrigeration
As technology advances, absorption refrigeration is likely to see improvements in efficiency and environmental impact. With growing interest in sustainable living and renewable energy, the future of absorption fridges looks promising and exciting.