TXV valve vs piston: what are the differences? Find out in this comprehensive guide as we provide a step-by-step comparison to help you make an educated choice.
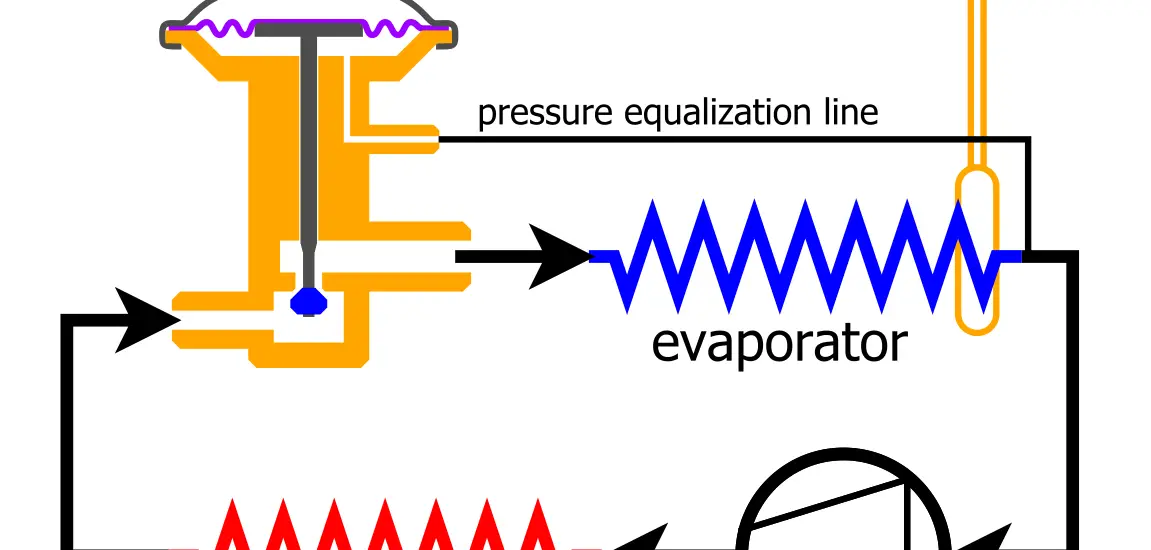
Table of Contents
What are TXV Valves and Pistons?
In your HVAC system, the evaporator coil is a critical element where the cooling of air takes place. The TXV (Thermal Expansion Valve) and the piston are both devices that control how much refrigerant gets into this evaporator coil. However, they do this in fundamentally different ways.
A TXV valve is a complex device that can adjust the flow of refrigerant based on the system’s cooling needs. It consists of several parts, including a diaphragm, spring, and thermal bulb. It is often used in systems where efficiency and precise control are desired.
Conversely, a piston is a simpler device that functions like a pinhole. It allows a set amount of refrigerant to flow through, regardless of the system’s current needs. Generally found in smaller, less complex systems, pistons are durable and straightforward.
How Do TXV Valves Work?
The TXV valve adjusts the refrigerant flow based on the system’s needs, providing a more flexible and efficient cooling process. It utilizes a thermal bulb filled with refrigerant, positioned at the evaporator coil’s outlet.
This bulb senses the coil’s temperature and adjusts the diaphragm in the valve, allowing more or less refrigerant to enter the evaporator coil. This adaptation ensures that the exact amount of cooling takes place, reducing energy wastage and improving efficiency.
Imagine you are baking cookies. A TXV valve would be like a smart oven that knows exactly when to turn up the heat and when to lower it, based on how the cookies are baking. This results in perfectly baked cookies every time.
How Do Pistons Work?
A piston doesn’t have any mechanism to adjust to the system’s varying cooling demands. It’s essentially like a small hole, the size of which is fixed.
Imagine you are watering a plant with a watering can. Regardless of how much water the plant actually needs, the can will always dispense water at the same rate, determined by the size of its spout.
Similarly, a piston allows a constant amount of refrigerant to flow through, potentially leading to inefficiencies during low-demand or high-demand periods.
Check out these other articles…
Expansion Valve Test: How to Perform in 7 Easy Steps
Where is the AC Expansion Valve Located? Comprehensive Guide
How Expansion Valve Works in Car AC: The Complete Breakdown
Expansion Work in Thermodynamics: A Comprehensive 411 Guide
Expansion Process in Thermodynamics: Comprehensive 411 Guide
TXV Valve vs Piston: Efficiency
Efficiency is often one of the main considerations when choosing between a TXV valve and a piston. A TXV valve is generally more efficient due to its ability to adapt to different cooling needs. This adaptability translates into energy savings, especially in fluctuating temperatures or load conditions. You could potentially see a reduction in your energy bills over time.
In contrast, systems with pistons can sometimes waste energy by overcooling or undercooling because they cannot adapt to changing conditions. Think of it as using a sledgehammer to crack a nut—effective, perhaps, but far from efficient.
TXV Valve vs Piston: Costs
While TXV valves offer better efficiency, they come with a higher initial price tag. The complexity of the device and the increased labor for installation contribute to this cost. If you’re looking for long-term savings and are willing to make a bigger upfront investment, a TXV valve might be more suitable for you.
On the other hand, pistons are generally less expensive upfront. They’re simpler devices, and installation is often quicker and less labor-intensive. However, the potential for higher energy consumption means that you might end up paying more in the long run.
