Ammonia water absorption refrigeration systems have been making waves in the world of cooling. With energy efficiency on everyone’s mind, these systems provide a greener alternative to traditional vapor-compression systems. But what makes ammonia so special, and how do these systems work? We’ll answer all these questions and more!
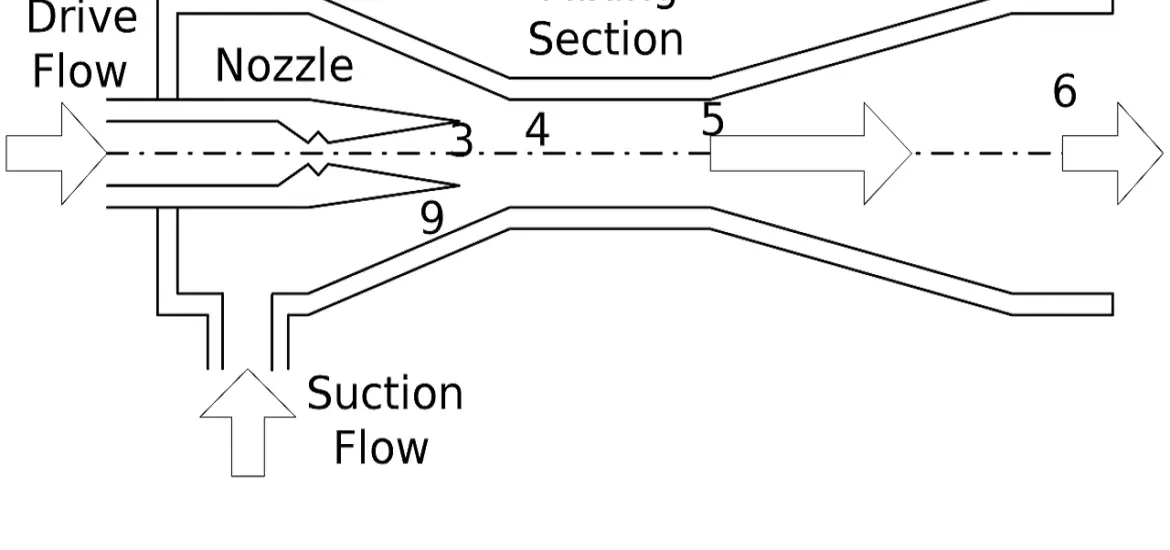
Table of Contents
Overview of Absorption Refrigeration Systems
So, what exactly are absorption refrigeration systems? These systems use a heat-driven cycle to provide cooling, which makes them a perfect candidate for harnessing waste heat or solar energy. They’re quite different from conventional vapor-compression systems, which rely on mechanical work to drive the cooling process.
The Need for Energy-efficient Cooling Solutions
As global temperatures rise and energy demand soars, we need to find more efficient ways to cool our homes, offices, and industries. Absorption refrigeration systems, like ammonia water absorption systems, are a step in the right direction for reducing our reliance on electricity and embracing renewable energy sources.
Comparison of Absorption Refrigeration Systems to Traditional Vapor-compression Systems
Traditional vapor-compression systems have been the go-to cooling solution for decades, but they come with a heavy carbon footprint. Absorption refrigeration systems, on the other hand, can harness waste heat or solar energy to provide cooling, making them an eco-friendly alternative. So why not switch to a greener cooling solution?
The Role of Ammonia in Absorption Refrigeration
Ammonia plays a crucial role in these systems, acting as the refrigerant. But what makes ammonia such an excellent candidate for this job?
Characteristics of Ammonia as a Refrigerant
Ammonia has a few unique properties that make it an ideal refrigerant: it’s got a low boiling point, a high heat of vaporization, and it’s chemically compatible with water. These characteristics allow it to effectively absorb and release heat in the refrigeration cycle.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Ammonia
While ammonia is an efficient refrigerant with a low environmental impact, it’s not without its drawbacks. It can be toxic and flammable, which means safety measures are a must. But with proper handling and precautions, the benefits of using ammonia in absorption refrigeration systems can far outweigh the risks.
Components of an Ammonia Water Absorption Refrigeration System
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s take a closer look at the inner workings of an ammonia water absorption refrigeration system. These systems consist of several key components, each playing a vital role in the cooling process.
The Evaporator
The evaporator is where the magic happens, and it all starts with the refrigerant—ammonia, in this case.
Function and Importance of the Evaporator
In the evaporator, ammonia vapor absorbs heat from the surrounding environment, causing the liquid refrigerant to evaporate. This heat absorption cools the area, making the evaporator a critical part of the refrigeration process.
Evaporation Process in Ammonia-water Systems
Ammonia and water are used in a unique combination in these systems. The ammonia-water mixture has a lower vapor pressure than pure ammonia, allowing the system to operate at lower pressures while maintaining efficient cooling. The evaporation process in these systems is crucial for achieving the desired cooling effect.
The Absorber
Once the ammonia vapor has done its job in the evaporator, it needs to be absorbed back into the water to continue the cycle.
Absorption of Ammonia Vapor
The absorber is designed to facilitate the absorption of ammonia vapor into the water. This step is essential for maintaining the low pressure in the evaporator and ensuring the system’s continuous operation.
Concentration Gradients and Mass Transfer in the Absorber
In the absorber, the concentration gradient between the ammonia-rich vapor and the ammonia-poor water drives mass transfer, allowing the ammonia to be absorbed into the water. This process keeps the refrigeration cycle going and maintains the system’s cooling efficiency.
The Generator
Now that the ammonia has been absorbed back into the water, it’s time to separate them once again and prepare for the next cycle.
Heating the Ammonia-water Solution
The generator heats the ammonia-water solution, causing the ammonia to evaporate and separate from the water. This step is crucial for regenerating the refrigerant and maintaining the system’s efficiency.
Separating Ammonia from Water in the Generator
As the ammonia evaporates, it leaves behind a more concentrated ammonia-water solution. The separated ammonia vapor is then directed to the condenser, while the concentrated solution is returned to the absorber for reuse in the system.
The Condenser
The condenser plays a crucial role in turning the ammonia vapor back into a liquid, ready for the next cycle.
Function and Importance of the Condenser
In the condenser, the ammonia vapor releases heat and turns back into a liquid. This step is vital for maintaining the system’s pressure balance and ensuring continuous operation.
Condensation Process in Ammonia-water Systems
The ammonia vapor is cooled in the condenser, allowing it to release its heat and turn back into a liquid. This liquid ammonia is then directed to the evaporator, where it will once again absorb heat and evaporate, continuing the refrigeration cycle.
The Expansion Valve
Before the liquid ammonia can enter the evaporator, it needs to pass through the expansion valve.
Role of the Expansion Valve in the Refrigeration Cycle
The expansion valve helps regulate the flow of liquid ammonia into the evaporator, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and maintains the desired cooling effect.
Types of Expansion Valves used in Ammonia Absorption Systems
There are several types of expansion valves used in ammonia absorption systems, including thermostatic expansion valves and electronic expansion valves. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, but the overall goal is to control the flow of liquid ammonia and maintain the system’s efficiency.
Read our other articles on absorption refrigeration – Absorption Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Understanding It
Absorption Ammonia Refrigeration System Performance
Now that we’ve explored the components of an ammonia water absorption refrigeration system let’s take a look at how we can measure their performance and efficiency.
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
When it comes to refrigeration systems, the Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a crucial indicator of efficiency. The COP tells us how much cooling effect we get from the system for each unit of energy input. The higher the COP, the more efficient the system.
Definition and Importance of COP
The COP is calculated by dividing the cooling capacity of the system by the amount of energy input required to achieve that cooling effect. By comparing the COP of different systems, we can make informed decisions about which system is the most efficient and environmentally friendly choice.
Factors Affecting the COP of an Ammonia Absorption System
Several factors can impact the COP of an ammonia absorption system, including the temperature of the heat source, the system’s design, and the operating conditions. By optimizing these factors, we can maximize the system’s efficiency and minimize its environmental impact.
System Efficiency
When comparing ammonia absorption systems to traditional vapor-compression systems, it’s essential to consider their overall efficiency.
Comparison of Ammonia Absorption System Efficiency to Vapor-compression Systems
While ammonia absorption systems may have a lower COP than traditional vapor-compression systems, they can still be more efficient overall when considering their ability to harness waste heat or solar energy. This means that ammonia absorption systems can be a more sustainable choice for certain applications.
Methods to Improve Efficiency in Ammonia Absorption Systems
There are several ways to boost the efficiency of ammonia absorption systems, including optimizing heat exchanger designs, using advanced control strategies, and integrating the system with other renewable energy sources like solar power or combined heat and power (CHP) systems.
Heat Exchanger Design
Heat exchangers play a vital role in ammonia absorption systems, helping to regulate the temperature and pressure within the system.
Role of Heat Exchangers in Ammonia Absorption Systems
Heat exchangers transfer heat between the various components of the system, ensuring that the refrigeration cycle runs smoothly and efficiently. They are crucial for maintaining the system’s performance and reliability.
Types of Heat Exchangers Used and their Influence on System Performance
Different types of heat exchangers, such as plate, shell-and-tube, and microchannel designs, can be used in ammonia absorption systems. The choice of heat exchanger can have a significant impact on system performance, so it’s essential to select the most appropriate design for the specific application.
Applications of Absorption Chiller Ammonia Systems
Ammonia absorption systems are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, from industrial processes to commercial buildings.
Industrial Applications
Ammonia absorption systems are well-suited for various industrial applications where efficient cooling and waste heat utilization are essential.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, ammonia absorption systems can provide efficient cooling for processes such as freezing, chilling, and refrigerated storage. Their ability to harness waste heat from other processes makes them an eco-friendly choice for this sector.
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
Ammonia absorption systems can also be used for cooling in chemical and pharmaceutical production processes, where precise temperature control and energy efficiency are critical. By using waste heat from these processes, ammonia absorption systems help minimize the overall energy consumption and environmental impact.
Commercial Applications
Commercial buildings can also benefit from the energy efficiency and environmental friendliness of ammonia absorption systems.
Air Conditioning in Large Buildings
Ammonia absorption systems are an excellent choice for air conditioning in large commercial buildings, such as offices, hotels, and shopping malls. By using waste heat or renewable energy sources, these systems can significantly reduce the building’s energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Data Center Cooling
Data centers generate a considerable amount of heat that needs to be removed to ensure the proper functioning of equipment. Ammonia absorption systems can provide efficient cooling while utilizing waste heat, making them an environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution for data center cooling.
Sustainable Energy Applications
Ammonia absorption systems can be integrated with sustainable energy sources for even more eco-friendly cooling solutions.
Solar and Waste Heat-driven Ammonia Absorption Systems
By harnessing solar energy or waste heat from other processes, ammonia absorption systems can operate with minimal additional energy input. This makes them an attractive option for sustainable cooling in various applications, from industrial processes to commercial buildings.
Integration with Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems
Ammonia absorption systems can also be integrated with combined heat and power (CHP) systems, which generate both electricity and heat from a single fuel source. By using the waste heat from CHP systems, ammonia absorption systems can provide efficient and sustainable cooling solutions.
Safety and Environmental Considerations for Ammonia Absorption Systems
While ammonia absorption systems offer many benefits, it’s essential to address the safety and environmental concerns associated with using ammonia as a refrigerant.
Ammonia Safety
Ammonia is both toxic and flammable, so proper precautions and safety measures must be in place when using ammonia absorption systems.
Toxicity and Flammability Concerns
Ammonia can be harmful if inhaled, ingested, or if it comes into contact with the skin. Its flammability also poses a risk of fire or explosion under certain conditions. These concerns can be mitigated through proper system design, maintenance, and safety protocols.
Safety Guidelines and Best Practices
Following established safety guidelines and best practices, such as proper ventilation, leak detection, and emergency response plans, can help minimize the risks associated with using ammonia as a refrigerant in absorption systems.
Environmental Impact
Ammonia has a low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP), making it an environmentally friendly refrigerant. However, it’s essential to take steps to prevent ammonia leaks and minimize any potential environmental risks.
Ammonia’s Low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP)
Unlike some other refrigerants, ammonia does not contribute significantly to global warming or ozone depletion. This makes it an attractive option for those looking to minimize their environmental impact.
Mitigating Ammonia Leaks and Reducing Environmental Risks
By implementing leak detection systems, regular maintenance, and proper system design, the risk of ammonia leaks can be minimized, reducing any potential environmental risks associated with using ammonia as a refrigerant.
Future Developments in Absorption Chiller Ammonia Systems
As the demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly cooling solutions continues to grow, so too will the development of ammonia absorption systems.
Technological Advancements
Future developments in ammonia absorption systems will likely focus on improving system efficiency, creating compact and modular designs, and integrating with other renewable energy sources.
Improvements in System Efficiency
Technological advancements will continue to enhance the efficiency of ammonia absorption systems. These improvements may include more effective heat exchangers, advanced control strategies, and innovative system designs that maximize performance while minimizing energy consumption.
Compact and Modular designs
Future ammonia absorption systems may feature compact and modular designs, making them more accessible and adaptable for various applications. These designs can help reduce installation and maintenance costs while offering greater flexibility for different cooling needs.
Market Trends and Growth
The increasing demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions will likely drive the growth and adoption of ammonia absorption systems worldwide.
Increasing Demand for Energy-efficient Cooling Solutions
As concerns about energy consumption and climate change continue to grow, the demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly cooling solutions like ammonia absorption systems will only increase. This growing demand will drive further innovation and development in the field.
Global Adoption of Ammonia Absorption Systems
As the benefits of ammonia absorption systems become more widely recognized, we can expect to see increased adoption of these systems globally. This growth will be driven by both the need for more energy-efficient cooling solutions and the desire to reduce the environmental impact of cooling systems.
In conclusion, ammonia water absorption refrigeration systems offer a unique, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly solution for various cooling applications. By understanding the components, performance, and safety considerations associated with these systems, we can make informed decisions and embrace their potential for a more sustainable future.