In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn all you need to know about the expansion valve in AC systems
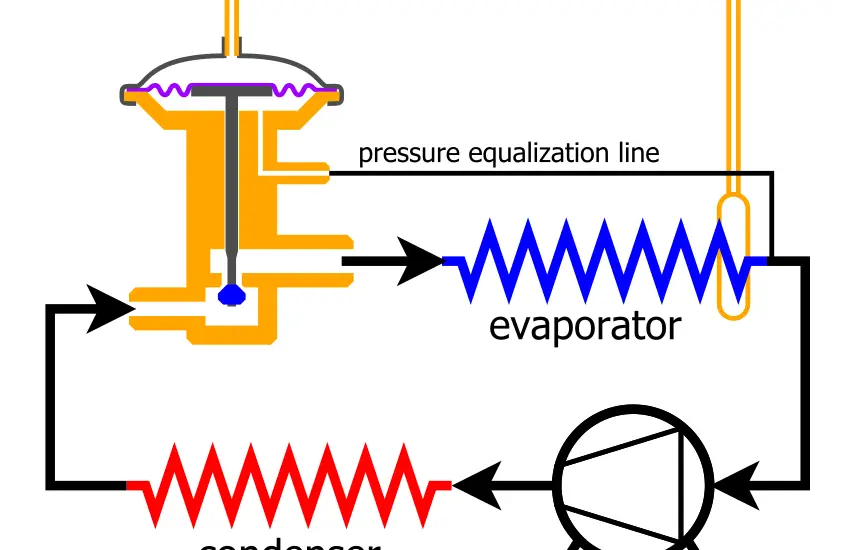
Table of Contents
What Is the Expansion Valve in AC?
The expansion valve, also known as the thermostatic expansion valve or TXV, is a pivotal component of any air conditioning system. It is primarily designed to regulate and control the amount of refrigerant that enters the evaporator coil.
The main function of an expansion valve in AC is to meticulously control the rate at which the refrigerant flows into the evaporator, thereby ensuring that the right amount of cooling is achieved in line with the cooling demands of the system. This precise control enhances the overall efficiency of your air conditioner, ensuring optimal operation.
How Does the Expansion Valve in AC Systems Work?
The operation of an air conditioning system may seem complex, but it can be broken down into simpler steps for easy understanding.
The refrigerant moves through the compressor, where it is heated and pressurized. This high-pressure gas then travels to the condenser.
In the condenser, the refrigerant is cooled down and condensed into a high-pressure liquid. The expansion valve then comes into play, receiving this liquid and dropping its pressure significantly. This sudden drop in pressure causes the refrigerant to partially evaporate, leading to a substantial drop in temperature.
The refrigerant, now a low-pressure mixture of liquid and gas, is ready to move into the evaporator. In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding air, thereby producing the cooling effect associated with air conditioning systems.
Expansion Valve or Compressor: Which is More Important?
It’s common to question which component is more critical – the expansion valve or the compressor. The truth is, both are of paramount importance to your AC system’s operation.
The compressor and expansion valve work hand in hand, harmoniously collaborating to achieve the desired cooling effect. The compressor’s role is to pressurize the refrigerant, preparing it for the condensing process, while the expansion valve controls its flow into the evaporator, maintaining a balance in the system.
Therefore, it isn’t a case of one being more important than the other – both are integral for achieving efficient and effective cooling.
Check out these other related articles…
Expansion Valve Types: Your Comprehensive Guide
Expansion Valve in Refrigerator: Your Easy 101 Guide
Expansion Valve Function: Easy 101 Guide
Expansion Valve Chiller: Your Quick 101 Guide
How Does an Expansion Valve Work: Your Easy 101 Guide
How to Recognize a Faulty Expansion Valve in AC
Recognizing a faulty expansion valve in an air conditioner can save you a great deal of discomfort during hot summer days. A malfunctioning expansion valve can interfere with the regular cooling pattern of your AC system.
Common symptoms of a faulty expansion valve include inadequate cooling, frost or ice buildup on the evaporator coil, and erratic cooling patterns.
Should you notice any of these symptoms, it is advisable to reach out to an HVAC professional who can inspect your system. They can confirm if the problem lies with the expansion valve or another component of the system and recommend the necessary repairs or replacements, thereby saving you from further discomfort and unnecessary costs.
Conclusion
The role of the expansion valve in AC systems, while not always at the forefront of discussions, is vital for the efficient operation of the cooling process. By controlling the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, it ensures the AC system performs at its best.
So, next time your AC is running, remember the vital role played by the humble expansion valve in maintaining your comfort.