Refrigeration in thermodynamics might sound like a complex topic, but it’s actually all around us in our daily lives. Ever wonder how your fridge keeps your food fresh, or how your air conditioner keeps your home cool? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of refrigeration and see how it impacts you as a homeowner.
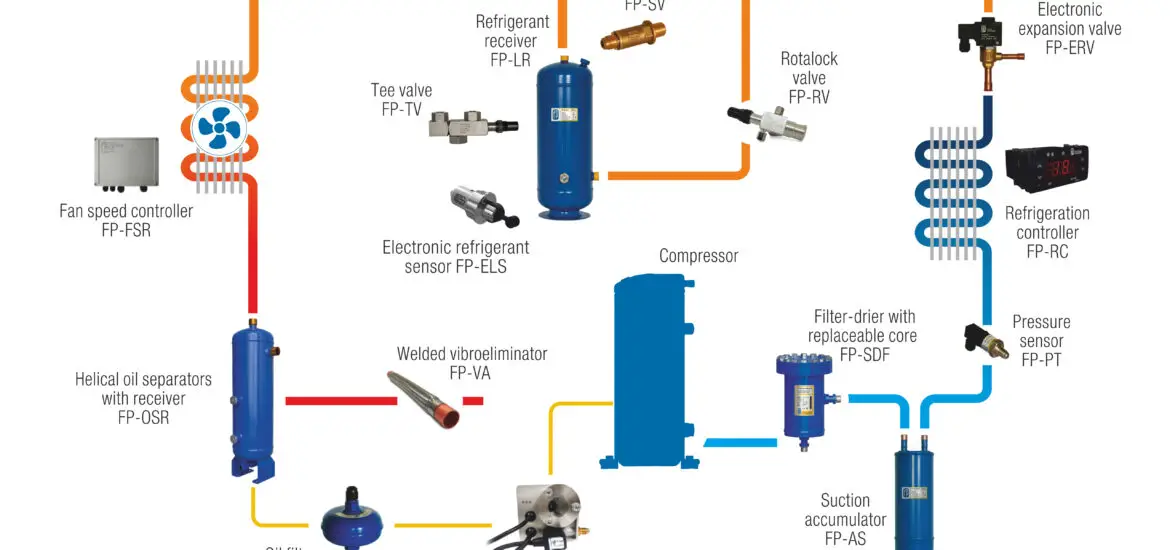
Table of Contents
Introduction to Refrigeration
Simply put, refrigeration is the process of removing heat from a space, substance, or system to keep it cool. It’s like giving heat the cold shoulder! Cool, right?
Importance of refrigeration
Refrigeration is essential for preserving food, making sure your home stays comfortable, and even keeping your computer from overheating. It’s like a superhero, swooping in to save the day!
Applications of refrigeration
From fridges and freezers to air conditioners and heat pumps, refrigeration plays a crucial role in keeping our homes and lives running smoothly. Can you imagine a world without it?
Basics of Thermodynamics
Laws of thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is the study of heat and energy, and it’s governed by four key laws. These laws help us understand how energy moves and changes in our world, and they’re the foundation for understanding refrigeration.
Heat and temperature
Heat is energy in motion, while temperature measures the average energy of particles in a substance. When heat flows, it’s like a dance party happening between atoms and molecules!
Work and energy
In thermodynamics, work is the transfer of energy from one system to another. Think of it like passing a hot potato from one person to another. Energy, on the other hand, is the capacity to do work. It’s the fuel that keeps the party going!
Entropy
Entropy is a measure of disorder in a system. When heat flows, entropy increases, and things get messier. But don’t worry, refrigeration helps keep things in check and maintain order in your home!
Click here for more articles on vapor compression.
Refrigeration Cycles
Vapor Compression Cycle
Components of a vapor compression cycle
This cycle is like the beating heart of your fridge or air conditioner. It has four main parts:
- Compressor: This is the “pump” that pushes refrigerant through the system.
- Condenser: Here, the refrigerant releases heat and turns from gas to liquid.
- Expansion valve: This nifty little device reduces pressure and cools the refrigerant even more.
- Evaporator: In this final stage, the refrigerant absorbs heat from its surroundings and turns back into a gas.
Phases of a vapor compression cycleThe vapor compression cycle goes through four main phases, like a well-choreographed dance:
- Compression: The refrigerant is compressed, raising its pressure and temperature.
- Condensation: The hot refrigerant releases heat as it changes from gas to liquid in the condenser.
- Expansion: The refrigerant’s pressure is reduced, and it cools down further in the expansion valve.
- Evaporation: The refrigerant absorbs heat from its surroundings and evaporates, starting the cycle all over again.
Efficiency and performance of vapor compression cycles
The efficiency of a vapor compression cycle is measured by two key metrics: the coefficient of performance (COP) and the energy efficiency ratio (EER). Higher numbers mean better performance, so you’ll want to look for appliances with high COP and EER ratings to get the best bang for your buck!
Absorption Refrigeration Cycle
Components of an absorption cycle
Absorption refrigeration is an alternative to vapor compression, and it has its own set of components:
- Absorber: This is where the refrigerant gets absorbed by a special solution.
- Generator: Here, heat is applied to separate the refrigerant from the solution.
- Expansion valve: Just like in the vapor compression cycle, this reduces pressure and cools the refrigerant.
- Evaporator: Once again, the refrigerant absorbs heat and evaporates, keeping things cool.
Working principle of an absorption cycle
The absorption cycle uses heat and a special solution to move the refrigerant through the system, rather than a compressor. It’s like a friendlier, more eco-conscious version of the vapor compression cycle!
Advantages and disadvantages of absorption refrigeration
Absorption refrigeration has some great perks, like being quieter and more environmentally friendly. However, it’s usually less efficient than vapor compression and can be more expensive to install. It’s all about weighing the pros and cons to find the best fit for your needs!
Applications of absorption refrigeration
Absorption refrigeration is commonly used in large-scale commercial settings, like hotels and hospitals, as well as in off-grid situations where electricity is limited. Who knew refrigeration could be so versatile?
Gas Refrigeration Cycle
Components of a gas refrigeration cycle
This type of refrigeration cycle is a bit different, with three main components:
- Compressor: Just like in the vapor compression cycle, this is the “pump” that moves the refrigerant.
- Heat exchanger: This device transfers heat from one fluid to another without mixing them.
- Expansion turbine: The refrigerant expands and cools down as it flows through this turbine.
Working principle of a gas refrigeration cycle
The gas refrigeration cycle uses a high-pressure gas as the refrigerant, which is compressed, cooled in the heat exchanger, and then expanded through a turbine to lower its temperature even more. It’s a unique spin on the refrigeration process that you might not have heard of before!
Applications of gas refrigeration
Gas refrigeration is typically used in specialized industries, such as aerospace and natural gas processing, where high cooling capacities and low temperatures are required. It might not be in your home, but it’s still a cool piece of refrigeration tech!
Refrigerants
Properties of Refrigerants
Thermal properties
A good refrigerant has certain thermal properties, like a low boiling point, high heat capacity, and high latent heat. It’s all about finding the perfect balance to keep things cool and efficient!
Environmental properties
Refrigerants can have an impact on our environment, so it’s important to consider factors like ozone depletion potential (ODP) and global warming potential (GWP). Going green is more important than ever, even when it comes to refrigeration!
Safety properties
Safety first! A good refrigerant should have low flammability and low toxicity, so you can keep your home cool without any worries.
Types of Refrigerants
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
CFCs were once popular refrigerants, but they’ve been phased out due to their high ODP and GWP. It’s like saying goodbye to an old friend who wasn’t so great for the environment.
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs)
HCFCs are a step up from CFCs, with lower ODP and GWP, but they’re still not the best choice for the environment. The search for greener options continues!
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
HFCs have zero ODP and lower GWP than CFCs and HCFCs, making them a more eco-friendly choice. They’re like the new kid on the block that everyone wants to be friends with!
Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs)
HFOs are a newer class of refrigerants with very low GWP, making them even more environmentally friendly. They’re paving the way for a greener future in refrigeration!
Natural refrigerants
Some refrigerants come straight from nature, like ammonia (NH3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and hydrocarbons (HCs). They’re like the eco-warriors of the refrigeration world, fighting for a cleaner, greener planet!
Advances in Refrigeration Technology
Magnetic Refrigeration
Magnetocaloric effect
Magnetic refrigeration relies on the magnetocaloric effect, which is a change in temperature caused by exposing certain materials to a magnetic field. It’s like using the power of magnets to keep things cool!
Components of a magnetic refrigeration system
A magnetic refrigeration system consists of a magnetocaloric material, a magnetic field source, and a heat exchange system. It’s a cutting-edge technology that could revolutionize the refrigeration industry!
Advantages and challenges of magnetic refrigeration
Magnetic refrigeration has some great advantages, like being environmentally friendly, energy-efficient, and potentially more reliable than traditional refrigeration systems. However, there are still some challenges to overcome, like high costs and limited availability of magnetocaloric materials.
Thermoacoustic Refrigeration
Thermoacoustic effect
Thermoacoustic refrigeration uses sound waves to create a temperature difference and move heat. It’s like using the power of music to keep things cool!
Components of a thermoacoustic refrigeration system
A thermoacoustic system consists of a sound generator, a resonator, and a heat exchanger. These parts work together in harmony to create a unique and efficient refrigeration process.
Advantages and challenges of thermoacoustic refrigeration
Thermoacoustic refrigeration has some awesome benefits, like being eco-friendly, having fewer moving parts, and being potentially more reliable than traditional systems. However, it’s still a developing technology with some challenges, like lower efficiency and higher initial costs.
Cryogenic Refrigeration
Cryogenic temperatures
Cryogenic refrigeration deals with extremely low temperatures, typically below -150°C (-238°F). It’s like stepping into a whole new world of cold!
Techniques for cryogenic refrigeration
There are a few techniques used in cryogenic refrigeration, like the Joule-Thomson effect and adiabatic demagnetization. These methods allow us to achieve ultra-low temperatures for specialized applications.
Applications of cryogenic refrigeration
Cryogenic refrigeration is used in fields like space exploration, medicine, and research, where extremely low temperatures are needed. It’s a fascinating and specialized branch of refrigeration!
Conclusion
Importance of refrigeration in modern society
Refrigeration is an essential part of our lives, keeping our food fresh, our homes comfortable, and our technology running smoothly. It’s a behind-the-scenes hero that we couldn’t live without!
Future trends and developments in refrigeration technology
As we look to the future, new refrigeration technologies like magnetic and thermoacoustic refrigeration offer exciting possibilities for greener, more efficient cooling systems. The world of refrigeration is ever-evolving, and we can’t wait to see what’s in store!