Ever wondered how a vapor absorption refrigeration system using three fluids could make your home more energy-efficient and eco-friendly? Let’s dive into the world of this innovative technology, and find out how it works and how it could benefit you as a homeowner.
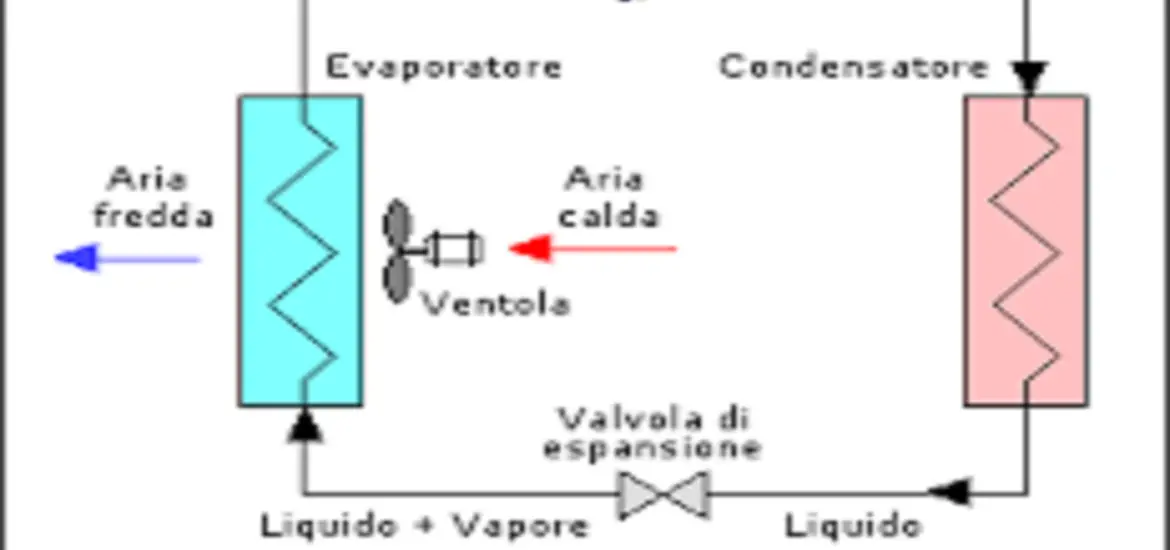
Table of Contents
Overview of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration
Basic principles
At its core, vapor absorption refrigeration is a cooling process that relies on the absorption of a refrigerant by another fluid, known as the absorbent. This process creates a cooling effect, perfect for keeping your home comfy and cool in those hot summer months.
Comparison with vapor compression refrigeration
How does vapor absorption refrigeration compare to the more common vapor compression refrigeration? Well, while both systems achieve cooling, vapor absorption refrigeration uses heat energy instead of mechanical energy, making it more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient.
Read more about vapor refrigeration here: Vapor Refrigeration: Easy Guide to Keeping Things Chill
Types of absorption systems
There are two main types of absorption systems: single-fluid and three-fluid. Our focus today is on the three-fluid system, which offers better performance and higher efficiency than its single-fluid counterpart.
Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System Using Three Fluids (Three-fluid System)
Advantages
So, what makes a three-fluid system so special? First off, it offers higher efficiency and flexibility, which means you’ll save money on your energy bills. Secondly, it’s more environmentally friendly, thanks to its use of low-GWP (global warming potential) refrigerants and waste heat.
Applications
Three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems are not only for industrial and commercial use, but they’re also suitable for residential applications like solar-driven refrigeration and heat-driven cooling systems, making them a great option for eco-conscious homeowners.
Components of a Three-Fluid Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System
Absorber
Function
The absorber is where the magic happens: it’s the component that absorbs the refrigerant vapor, creating that all-important cooling effect. It’s kind of like a sponge, soaking up the heat from your home!
Design considerations
When designing an absorber, factors like heat transfer, pressure drop, and material compatibility come into play. It’s important to get the right balance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Generator
Function
The generator is responsible for separating the refrigerant from the absorbent solution. By applying heat, the generator causes the refrigerant to vaporize and move on to the condenser, while the absorbent is returned to the absorber. It’s like a big break-up, setting the refrigerant free to cool your home once more.
Heat sources
Generators can use various heat sources, including natural gas, solar energy, or even waste heat from other appliances in your home. That’s right, your refrigerator could help power your air conditioner!
Condenser
Function
The condenser’s job is to turn the refrigerant vapor from the generator back into a liquid, releasing heat in the process. This heat can then be expelled outside, keeping your home cool and fresh.
Types of condensers
There are several types of condensers to choose from, including air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condensers. Each has its pros and cons, so it’s essential to pick the one that best suits your needs and your home’s environment.
Evaporator
Function
Now we’ve reached the evaporator, where the refrigerant absorbs heat from your home and evaporates back into a vapor. This process creates the cooling effect, making your living space comfortable and inviting.
Types of evaporators
There are various evaporators available, such as direct expansion, flooded, or plate heat exchangers. The choice depends on factors like efficiency, cost, and your home’s specific requirements.
Expansion device
Function
The expansion device regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It’s like a traffic cop, making sure everything flows smoothly and efficiently through the system.
Types of expansion devices
Common expansion devices include thermostatic expansion valves, capillary tubes, and float valves. Each offers different levels of control and responsiveness, so it’s crucial to choose the right one for your system.
Solution heat exchanger
Function
The solution heat exchanger is an essential part of the system, transferring heat between the absorbent solution and the refrigerant. This heat transfer improves the system’s efficiency, saving you even more on your energy bills.
Design considerations
When designing a solution heat exchanger, it’s vital to consider factors like the heat transfer rate, pressure drop, and material compatibility. The goal is to maximize efficiency while minimizing energy loss and potential maintenance issues.
Pump
Function
The pump circulates the absorbent solution between the absorber and the generator, ensuring a continuous flow and maintaining the system’s efficiency.
Types of pumps
There are various pumps available, including centrifugal, reciprocating, and diaphragm pumps. The choice depends on factors like flow rate, pressure requirements, and reliability.
Working Principle of a Three-Fluid Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System
Overview
Explanation of the refrigeration cycle
Now that we’ve covered the components, let’s look at how they all work together to create that wonderful cooling effect. The refrigeration cycle consists of absorption, desorption, condensation, and evaporation processes, all working in harmony to keep your home comfortable.
Three-fluid system
Fluid roles
In a three-fluid system, there are three key players: the refrigerant, the absorbent, and the inert gas. The refrigerant is responsible for the cooling, the absorbent soaks up the refrigerant vapor, and the inert gas helps maintain pressure and optimize performance.
Cycle steps
The three-fluid system follows a specific sequence of steps, including absorption, desorption, condensation, and evaporation. By understanding how these steps work together, you can appreciate the genius behind this innovative cooling technology.
Heat and mass transfer
Absorption process
The absorption process is all about the refrigerant vapor being absorbed by the absorbent. This process extracts heat from your home, creating a cooling effect. It’s like taking a cold shower on a hot day, except your house is the one cooling down!
Desorption process
The desorption process involves the generator applying heat to the absorbent-refrigerant solution, causing the refrigerant to vaporize and separate from the absorbent. Think of it as the steam rising from a hot cup of tea, taking the heat with it.
Selection of Fluids for a Three-Fluid Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System
Refrigerants
Criteria for selection
When choosing a refrigerant, factors like safety, environmental impact, and compatibility with the absorbent and inert gas must be considered. After all, you want a refrigerant that’s safe and efficient, right?
Common refrigerants
Some popular refrigerants include ammonia, water, and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). Each has its pros and cons, so it’s crucial to pick the right one for your system and your home’s needs.
Absorbents
Criteria for selection
When selecting an absorbent, you need to consider factors like its affinity for the refrigerant, stability, and heat transfer properties. A good absorbent can make all the difference in your system’s performance.
Common absorbents
Some widely used absorbents include lithium bromide, water, and ionic liquids. Each offers different benefits and drawbacks, so choose wisely!
Inert gas
Criteria for selection
The inert gas plays a crucial role in maintaining pressure and optimizing performance. When selecting an inert gas, consider factors like its ability to maintain a stable pressure, compatibility with other fluids, and cost-effectiveness.
Common inert gases
Some common inert gases include helium, nitrogen, and argon. Each has its unique properties, so it’s essential to find the one that best suits your system’s requirements.
Performance Evaluation and Enhancement Techniques
Performance indicators
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
One way to measure the performance of your vapor absorption refrigeration system is by looking at its Coefficient of Performance (COP). A higher COP means better efficiency, which translates to lower energy bills for you. Who wouldn’t want that?
Exergy efficiency
Another performance indicator is exergy efficiency, which measures how effectively your system utilizes the available energy. A higher exergy efficiency means better performance and more energy savings.
Performance enhancement techniques
Advanced heat exchangers
One way to boost your system’s performance is by using advanced heat exchangers, which can improve heat transfer and reduce energy loss. It’s like upgrading your car’s engine for better fuel efficiency.
Multiple-effect cycles
Another technique is to use multiple-effect cycles, which can increase the system’s COP and reduce energy consumption. It’s like getting more bang for your buck!
Heat recovery systems
Heat recovery systems are another great way to improve performance, as they utilize waste heat from other appliances in your home. You’ll be recycling heat, making your home even greener!
Ejector-assisted cycles
Ejector-assisted cycles can also enhance your system’s performance by reducing the load on the compressor, leading to lower energy consumption and improved efficiency. It’s like having an extra helping hand to lighten the load on your cooling system!
Applications of Three-Fluid Vapor Absorption Refrigeration Systems
Industrial applications
Food and beverage processing
Three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems can be used in food and beverage processing, where precise temperature control is essential. They help maintain food quality, extend shelf life, and keep your favorite snacks and drinks fresh and delicious.
Pharmaceutical industry
Pharmaceutical companies also benefit from using these systems, as they provide stable and consistent cooling for the production and storage of medicines. Your medications stay safe and effective, thanks to this cooling technology.
Commercial applications
Air conditioning systems
Commercial buildings can use three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems for their air conditioning needs. They offer efficient and sustainable cooling, keeping employees comfortable and productive.
Cold storage facilities
These systems are also ideal for cold storage facilities, where maintaining constant low temperatures is crucial for preserving perishable goods. They help reduce food waste and ensure products reach customers in peak condition.
Residential applications
Solar-driven refrigeration
For eco-conscious homeowners, solar-driven three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems are a fantastic option. They utilize solar energy to power the cooling process, reducing your home’s carbon footprint and energy costs.
Heat-driven cooling systems
Heat-driven cooling systems, powered by waste heat or renewable energy sources, are another great choice for homeowners looking to save on energy costs and make their homes more sustainable.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Emission reduction
Use of low global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants
By using low GWP refrigerants, three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, making a positive impact on the environment.
Use of waste heat and renewable energy sources
These systems can also utilize waste heat or renewable energy sources, like solar or geothermal energy, further reducing their environmental impact and making them a more sustainable cooling option.
Energy efficiency
Impact on energy consumption
Three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems can reduce energy consumption by operating more efficiently than traditional cooling systems, helping you save on energy costs and reduce your carbon footprint.
Energy conservation measures
By incorporating energy conservation measures, like advanced heat exchangers and heat recovery systems, these cooling systems can become even more energy-efficient, making them a top choice for eco-friendly homeowners.
Conclusion
Summary of key findings
In summary, three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems offer many advantages, such as increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and a lower environmental impact. They’re suitable for various applications, from industrial to residential settings.
Future prospects
As technology advances and the need for sustainable cooling solutions grows, we can expect these systems to become even more efficient and widespread, playing a significant role in our efforts to combat climate change and create a greener future for all.
Challenges and opportunities
Despite their many benefits, three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration systems face challenges, such as high initial costs, complex designs, and the need for ongoing research and development to optimize performance. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovation, improvement, and wider adoption of this environmentally-friendly cooling technology.
By considering the various factors discussed in this article, such as fluid selection, performance indicators, and applications, homeowners can make informed decisions when choosing a three-fluid vapor absorption refrigeration system. Embracing this sustainable cooling solution can help reduce energy costs, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and contribute to a more environmentally-friendly home.