Water cooled condenser refrigeration is one of those technical concepts that may seem a bit daunting at first, but don’t worry! We’re going to simplify it for you. This approach to refrigeration is quite ingenious, with water acting as the coolant. Intrigued? You should be!
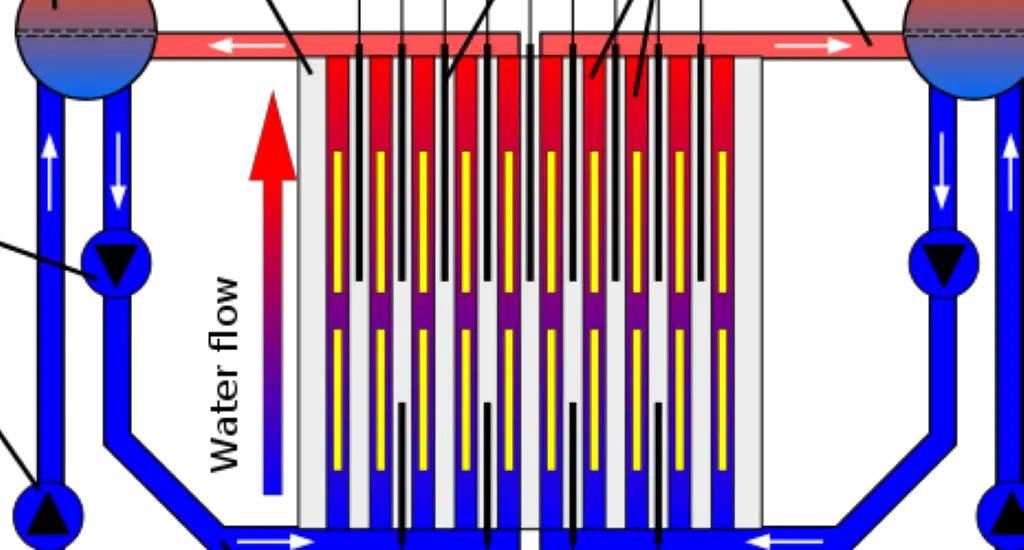
Table of Contents
Brief Understanding of Water Cooled Condenser Refrigeration
Imagine being in a sweltering room, holding an icy glass of lemonade. The coolness from the glass seeping into your hand is akin to the function of a water cooled condenser. In a refrigeration system, the condenser plays the vital role of releasing the heat carried by the refrigerant, and water, in this context, serves as the ultimate heat sink. It’s all about managing heat in a way that keeps your space or materials cool. Kinda cool, right?
Deep Dive into Water Cooled Condenser
Let’s embark on an exploration of the water cooled condenser, examining its unique features, components, and advantages as well as considerations.
Definition and Function of a Water Cooled Condenser
A water cooled condenser, as the name suggests, uses water to carry away the heat. It’s a bit like using a towel to wipe off sweat on a hot day. In essence, water does the heavy lifting of carrying away the heat released by the refrigerant.
Components of a Water Cooled Condenser
Under the hood of a water cooled condenser, you’ll find several key parts. A shell and tube system, for example, where the refrigerant flows through the shell, and water runs inside the tubes. It’s a smooth operation, like a well-choreographed dance, with each part playing its role to perfection.
The Role of Water in a Water Cooled Condenser
The star of the show in a water cooled condenser is, of course, water. It does the major job of soaking up the heat from the refrigerant. It’s like the refrigerant is passing the baton of heat to the water, which then goes on to release it elsewhere.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Water Cooled Condenser
Nothing’s perfect, and the same goes for water cooled condensers. Sure, they’re efficient and reliable, but there are always some drawbacks to keep in mind.
Efficiency of a Water Cooled Condenser
Water cooled condensers are like the efficient employees who never get tired. They offer higher efficiency than their air-cooled counterparts, especially in larger systems. But, remember the water is doing the hard work here!
Maintenance and Cost Factors
While efficient, water cooled condensers require more upkeep. They’re like a high-maintenance friend, needing regular cleaning and water treatment to prevent scale formation. Also, their upfront cost might be higher. So, it’s essential to consider these factors while opting for one.
The Working Principle of a Water Cooled Condenser
We’ll demystify the operational principles of a water cooled condenser, breaking down the cooling process into digestible chunks.
Detailed Process of a Water Cooled Condenser
The operation of a water cooled condenser isn’t too hard to understand. It’s like passing a hot potato (or in this case, heat) from one hand to another.
Refrigerant Cycle and Water Cooled Condenser
In a water cooled condenser, the refrigerant carrying heat from the system comes into the condenser. It’s like a runner entering the final stretch of a relay race, ready to pass on the baton of heat to water.
Heat Exchange Process in a Water Cooled Condenser
Heat exchange here is a simple game of ‘tag. The warm refrigerant releases its heat to the cooler water, which then carries it away. Just like that, your system is cooler!
Understanding the Phases of the Condensation Process
The condensation process isn’t a one-step wonder. It has three stages: desuperheating, condensing, and subcooling. It’s a bit like the process of making coffee: grind, brew, and then cool!
Desuperheating
Desuperheating is the stage where the superheated refrigerant gas starts losing heat and moves towards becoming a liquid. Think of it as cooling down after an intense workout session.
Condensing
Condensing is when the refrigerant, having lost enough heat, turns into a liquid. It’s the equivalent of settling down after a long day.
Subcooling
Lastly, subcooling is when the liquid refrigerant is cooled down below its condensation point. Consider it like getting that perfect chill on your drink.
Check out these other related articles…
How to Clean Refrigerator Condenser Coils: A Simple Guide
Condenser Fan and Compressor Not Running: 8 Proven Solutions
Types of Condensers: Your Comprehensive 411 Guide
Refrigerator Condenser Problems: 3 Proven Solutions
Evaporative Condenser: A Detailed Guide
Standard Water Cooled Condenser Refrigeration
Now, we’ll take a closer look at the standard water cooled condenser refrigeration, discussing its distinguishing features and where it’s typically employed.
Characteristics of a Standard Water Cooled Condenser
Standard water cooled condensers have certain attributes. Let’s get to know them a bit better.
Size and Capacity
Like choosing the right size of clothing, picking the appropriate size and capacity of your water cooled condenser is crucial. It directly impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
Design and Material Construction
The design and material of a water cooled condenser can vary. You’ll typically find shell and tube or coil designs, with materials ranging from copper to steel. It’s like choosing between jeans and trousers; it all depends on the application!
Temperature and Pressure Limits
Every water cooled condenser has certain temperature and pressure limits. It’s vital to operate within these boundaries for safety and durability. Think of them as speed limits on a highway; it’s best not to exceed them!
Application of Standard Water Cooled Condenser Refrigeration
Where can you find water cooled condensers in action? Let’s explore.
Industrial Uses
In industrial settings, water cooled condensers are often the go-to. They are used in factories, power plants, and large buildings. Picture a big operation that needs a lot of cooling. Yep, that’s where these guys shine.
Residential Uses
And it’s not just big industries. Water cooled condensers also find their way into residential cooling systems. It’s like having a mini cooling factory right in your home.
How Does a Water Cooled Condenser Work?
To wrap up, we’ll provide a step-by-step walk-through of a water cooled condenser at work and share important safety measures and operational best practices.
Step-by-Step Operation of a Water Cooled Condenser
So, what’s the step-by-step journey of heat in a water cooled condenser? Let’s follow the trail.
Inception of the Cooling Process
It all begins when the refrigerant enters the condenser, carrying heat from the system. It’s like stepping into a shower, ready to wash away the heat of the day.
Transfer of Heat to Water
Next up, the refrigerant comes into contact with the cooler water in the condenser. The heat jumps ship to the water, just like a hot day giving way to a cool night.
Expelling of Cooled Refrigerant
Finally, having lost its heat, the now-cooled refrigerant leaves the condenser, ready to do its cooling duty all over again. Imagine leaving an air-conditioned room, refreshed and cool. That’s what it’s like for the refrigerant!
Safety Measures and Best Practices in Operation
While water cooled condensers are efficient, it’s essential to follow some safety measures and best practices. After all, safety first, right?
Maintaining Optimal Water Flow
Keeping a check on the water flow in the condenser is like making sure your car has enough oil. It ensures the system operates smoothly and prevents overheating.
Preventing Overheating and Pressure Build-up
Overheating and pressure build-up in a water cooled condenser are like uninvited guests at a party; you want to avoid them. Regular checks and timely maintenance can help prevent such issues, ensuring your cooling system works like a charm.
