If you’re looking to understand the difference between an expansion valve vs capillary tube in a refrigeration system, this article is for you. We will explore both components, how they function, their similarities, and most importantly, the key differences. From cost to efficiency, this guide will help you grasp every aspect.
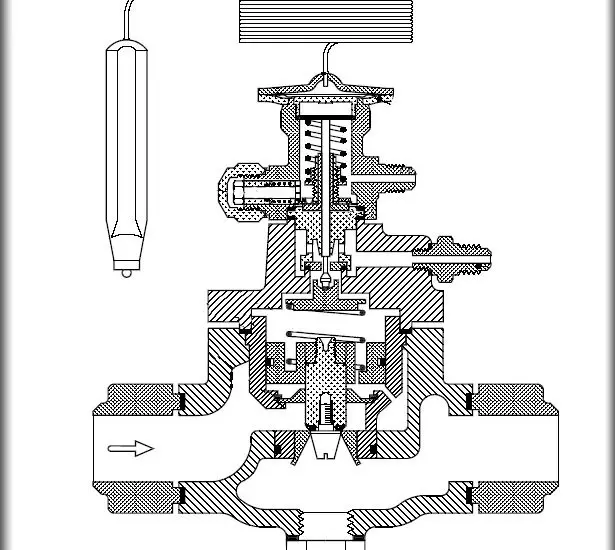
Table of Contents
What is an Expansion Valve?
An expansion valve is a device that regulates the flow of refrigerant within a refrigeration or air conditioning system. Here’s how it works:
Pressure Reduction: It reduces the high-pressure liquid refrigerant to a low-pressure, low-temperature mixture.
Temperature Control: By controlling the refrigerant flow, it ensures that the evaporator operates at the desired temperature.
Types: There are different types of expansion valves, such as thermostatic expansion valves (TXV) and electronic expansion valves (EXV), each with unique functionalities.
Adjustability: Unlike capillary tubes, expansion valves can be adjusted to match the system requirements, offering more control and efficiency.
What is a Capillary Tube?
A capillary tube is another form of throttling device used in smaller refrigeration systems. Here’s a closer look:
Design: It is a thin, long tube with a constant diameter, typically made of copper.
Function: It reduces the pressure of the refrigerant by forcing it through a narrow passage, thus cooling it down before it enters the evaporator.
Simplicity: Capillary tubes are simpler in design compared to expansion valves, without any adjustable parts, making them suitable for smaller, less complex applications.
Cost-Effective: Due to their simplicity, capillary tubes are generally less expensive but might be less efficient in some systems.
Check out these other related articles…
Clogged Expansion Valve Symptoms: A Complete Guide
How to Test Expansion Valve in 6 Easy Steps
Expansion Valve Troubleshooting: 4 Easy Steps to Follow
Electronic Expansion Valve Controller: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Expansion Valve? Your Ultimate Guide
Expansion Valve vs Capillary Tube: Key Differences
When comparing an expansion valve vs capillary tube, several critical differences must be considered. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions in the application of refrigeration or air conditioning systems:
Functionality
Expansion valves have the ability to be adjusted, allowing control over the flow of refrigerant, and adapting to various conditions within the system. Capillary tubes, on the other hand, are fixed in their function, providing a constant flow restriction.
The lack of adjustability in capillary tubes means they can’t adapt to changes in temperature or pressure, unlike expansion valves, which can be tuned to system demands.
Efficiency
Efficiency in controlling the refrigerant flow is vital for energy conservation and system performance. Expansion valves, being adjustable, can provide more precise control, which may result in higher efficiency, especially in larger or more complex systems.
Capillary tubes may lack this adaptability, and their efficiency may vary depending on the design and conditions of the particular system.
Cost
The complexity of the expansion valve’s design, which includes various moving parts, generally makes it more expensive to manufacture and install. Capillary tubes are simpler and thus more cost-effective.
While the initial cost might be lower for capillary tubes, it’s crucial to consider long-term efficiency and whether the cost-saving aligns with the performance needs of the specific application.
Application
Expansion valves are typically found in commercial and industrial refrigeration systems, where adjustability and precise control are necessary. Capillary tubes are commonly used in smaller, domestic applications like household refrigerators and window air conditioners.
The choice between the two often depends on factors such as system size, complexity, and the level of control required.
Maintenance
Maintenance requirements are another crucial difference. Expansion valves, with their complex structure and adjustable features, might require regular monitoring and potential adjustments or replacements of parts. Capillary tubes, being a simpler device with no moving parts, are virtually maintenance-free.
Consideration of ongoing maintenance, both in terms of time and cost, should be part of the decision-making process.
