Heat exchanger for refrigeration – sounds like a mouthful, right? But don’t fret! We’re here to break down the science behind it so you can understand how your home’s cooling system works. So, let’s get started!
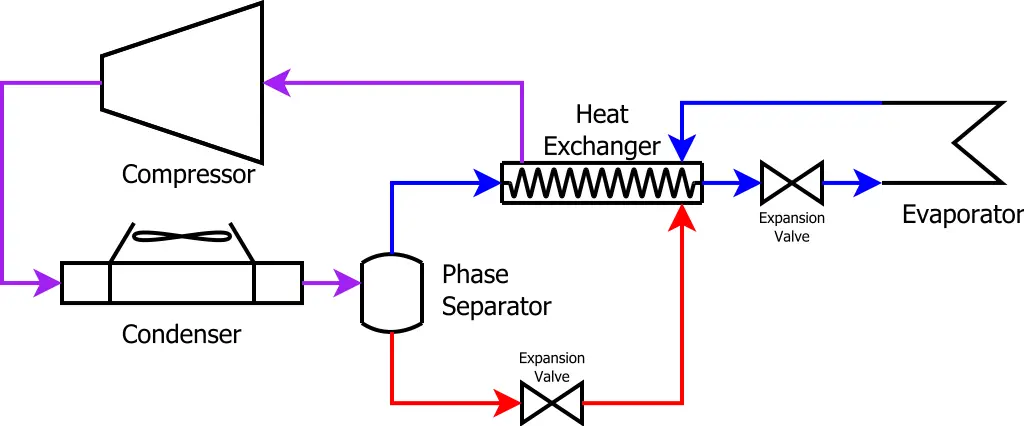
Table of Contents
Definition of a Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat from one medium to another without mixing the two. It’s a clever way to reuse energy and boost efficiency.
Functions of a Heat Exchanger
Heat exchangers have two main functions: heating and cooling. They can help regulate temperatures in your home and even save you money on energy bills. Cool, huh?
Types of Heat Exchangers
There are several types of heat exchangers, each with its unique design and purpose. Let’s take a look at some of the most common ones.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
These are the granddaddies of heat exchangers. They’ve been around for ages and are known for their durability and reliability. They consist of a shell housing containing many tubes where the heat exchange happens.
Plate Heat Exchangers
Imagine a stack of metal plates with grooves, and you’ve got a plate heat exchanger. They’re more compact than shell and tube exchangers, making them perfect for tight spaces.
Spiral Heat Exchangers
These exchangers use two flat, coiled plates to create a spiral path for fluids. They’re excellent at handling high pressures and can be super efficient, too.
Air-cooled Heat Exchangers
As the name suggests, these exchangers use air to cool fluids. They’re often used in refrigeration systems for their low maintenance and eco-friendly nature.
Heat Exchangers in Refrigeration Systems
Role of Heat Exchangers in Refrigeration
Cooling and Heating Processes
In a refrigeration system, heat exchangers play a crucial role in both the cooling and heating processes. They help remove heat from your home and keep you cool during those scorching hot days.
Energy Efficiency
Heat exchangers also help improve energy efficiency by transferring heat between different parts of the refrigeration cycle. This means less energy is wasted, and you save on energy bills!
Common Heat Exchangers in Refrigeration Systems
Now that we know what heat exchangers do, let’s look at the ones commonly found in refrigeration systems.
Evaporators
Evaporators absorb heat from the air and turn the refrigerant into a vapor. They’re essential for cooling your home.
Types of Evaporators
There are various types of evaporators, including natural convection, forced convection, and direct expansion. Each has its pros and cons, so it’s essential to choose the right one for your needs.
Functionality and Applications
Evaporators are used in a wide range of applications, from air conditioners to refrigerators and freezers. They help maintain comfortable temperatures in your home and keep your food fresh and safe.
Condensers
Condensers are the counterpart to evaporators. They release heat from the refrigerant, turning it back into a liquid and completing the refrigeration cycle.
Types of Condensers
There are several types of condensers, such as air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative. Each type has its benefits and drawbacks, so consider your specific needs when selecting a condenser.
Functionality and Applications
Condensers are found in many applications, from residential air conditioning systems to commercial refrigeration units. They’re crucial for maintaining an efficient and effective refrigeration cycle.
Design and Selection of Heat Exchangers for Refrigeration
Factors Affecting Design and Selection
Choosing the right heat exchanger for your refrigeration system is crucial. Here are some factors to consider:
Heat Transfer Requirements
Consider the heat transfer needs of your system. This will help you choose an exchanger with the appropriate capacity.
Space Constraints
Think about the available space for the heat exchanger. Some designs are more compact, making them ideal for tight spaces.
Material Compatibility
Consider the materials that will come into contact with the heat exchanger. Some materials may not be compatible and could cause corrosion or other issues.
Operating Conditions
Take into account the temperature and pressure conditions under which the heat exchanger will operate. This will help you select a suitable design and material.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Choose a heat exchanger that’s easy to maintain and clean. This will help ensure its longevity and performance.
Heat Exchanger Performance Metrics
To compare different heat exchangers, consider the following performance metrics:
Heat Transfer Coefficient
This measures how well a heat exchanger transfers heat. A higher coefficient means better heat transfer.
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient
This is a measure of the overall efficiency of a heat exchanger. It takes into account factors like material conductivity and fluid flow rates.
Pressure Drop
This is the decrease in pressure as fluids flow through the heat exchanger. A lower pressure drop means less energy is required to move the fluids, resulting in better efficiency.
Fouling Factor
Fouling occurs when dirt or debris builds up on the heat exchanger surfaces, reducing heat transfer efficiency. A lower fouling factor indicates a heat exchanger that’s less prone to fouling.
Materials and Construction of Typical Heat Exchanger for Refrigeration
Common Materials Used in Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers can be made from various materials, depending on their intended use and operating conditions. Let’s look at some common options.
Metals
Copper
Copper is an excellent heat conductor and is commonly used in heat exchangers. It’s also resistant to corrosion, making it a popular choice.
Aluminum
Aluminum is another common material used in heat exchangers. It’s lightweight and has excellent heat transfer properties. However, it may not be as durable as other metals, such as copper or stainless steel.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a popular choice for heat exchangers due to its corrosion resistance and strength. It may be more expensive than other metals, but it offers long-lasting performance and durability.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is often used in heat exchangers for its high strength and cost-effectiveness. However, it may be prone to corrosion, so proper maintenance is crucial.
Non-Metals
Plastics
Plastic heat exchangers are lightweight and corrosion-resistant. They’re often used in applications where chemical compatibility is essential, but they may not be as efficient as metal exchangers.
Ceramic
Ceramic heat exchangers offer excellent resistance to heat and chemicals, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. However, they can be brittle and prone to cracking, so careful handling is necessary.
Graphite
Graphite is a highly conductive material with excellent resistance to heat and chemicals. It’s often used in specialized applications, such as corrosive environments or high-temperature processes.
Heat Exchanger Construction Techniques
Heat exchangers can be constructed using various methods, depending on their design and materials. Here are some common techniques:
Welding
Welding is often used to join metal components in heat exchangers. It provides a strong bond and can be used with various materials, such as stainless steel and copper.
Brazing
Brazing is another method used to join metal parts in heat exchangers. It involves melting a filler metal between the components, which then solidifies to create a strong bond. Brazing is typically used with copper and aluminum exchangers.
Gaskets and Seals
Gaskets and seals are used to prevent leaks between components in heat exchangers. They can be made from various materials, such as rubber or silicone, depending on the application and operating conditions.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Heat Exchangers in Refrigeration Systems
Maintenance Guidelines
Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity and performance of your heat exchanger. Follow these guidelines to keep your exchanger in top shape:
Regular Inspection
Inspect your heat exchanger regularly for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Early detection can help prevent costly repairs or replacements.
Cleaning and Flushing
Clean and flush your heat exchanger periodically to remove debris and prevent fouling. This will help maintain optimal heat transfer efficiency.
Gasket and Seal Replacement
Replace worn or damaged gaskets and seals to prevent leaks and ensure proper functioning of your heat exchanger.
Corrosion Prevention
Take steps to prevent corrosion, such as using corrosion-resistant materials or applying protective coatings. This will help extend the life of your heat exchanger.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you’re experiencing issues with your heat exchanger, consider the following common problems and their solutions:
Reduced Heat Transfer Efficiency
Causes
Reduced efficiency can be caused by fouling, damaged components, or incorrect fluid flow rates. These issues can lead to decreased performance and higher energy costs.
Solutions
Regularly clean and inspect your heat exchanger to prevent fouling and identify damaged components. Adjust fluid flow rates as needed to maintain optimal efficiency.
Leakage
Causes
Leaks can occur due to worn or damaged gaskets and seals, corrosion, or cracked components. These issues can lead to decreased performance and potential damage to other system components.
Solutions
Inspect your heat exchanger for signs of leaks and replace any damaged gaskets or seals. Address corrosion issues promptly and consider using corrosion-resistant materials or coatings.
Excessive Pressure Drop
Causes
An excessive pressure drop can occur when there is a blockage or restriction in the heat exchanger, such as fouling or debris buildup. This can lead to decreased efficiency and increased energy consumption.
Solutions
Regularly clean and flush your heat exchanger to remove any debris or buildup. Ensure proper fluid flow rates and inspect for any blockages or restrictions.
Future Trends and Innovations in Heat Exchangers for Refrigeration
Energy-efficient Heat Exchangers
As energy efficiency becomes increasingly important, new heat exchanger designs and materials are being developed to improve performance and reduce energy consumption.
Compact Heat Exchangers
Compact heat exchangers are becoming more popular due to their ability to fit in tight spaces and offer high performance with a smaller footprint.
Smart Heat Exchangers
Smart heat exchangers incorporate sensors and control systems to monitor and optimize their performance, leading to improved efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
Waste Heat Recovery and Utilization
Waste heat recovery technologies, such as heat pumps and organic Rankine cycles, are being used in conjunction with heat exchangers to capture and reuse waste heat, further improving energy efficiency.