Refrigeration cycle with heat exchanger – sounds technical, right? But don’t worry, by the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of what it is and why it matters to you as a homeowner. At its core, the refrigeration cycle is a process that removes heat from a space or substance, keeping your home cool and your food fresh. Heat exchangers play a crucial role in this process, enhancing the efficiency of the refrigeration cycle. Let’s dive in and learn more about these essential components.
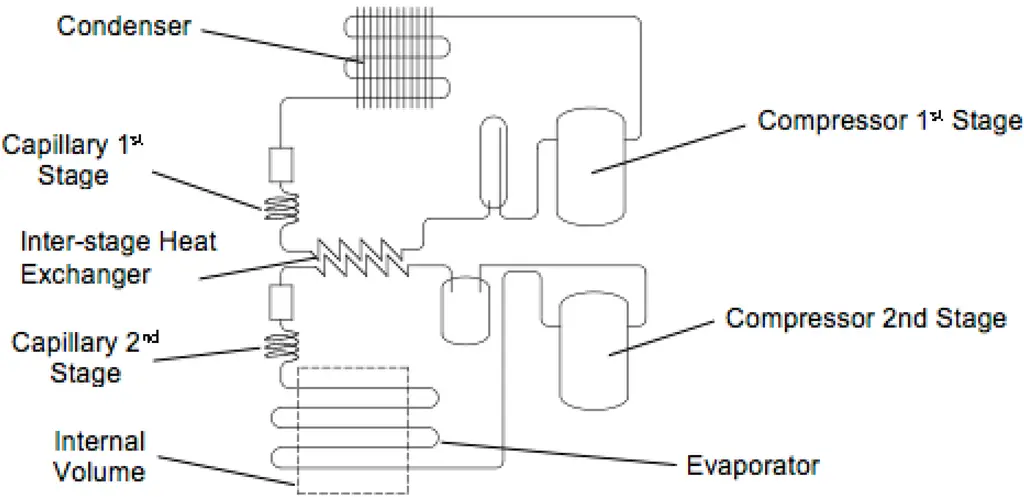
Table of Contents
Definition of refrigeration cycle
So, what exactly is the refrigeration cycle? In simple terms, it’s a process that takes heat away from a space or substance. This is the magic behind air conditioning, food preservation, and various industrial processes. It’s like a superhero, keeping your home comfortable and your food safe to eat.
Purpose of heat exchangers
Now, let’s talk about heat exchangers. These devices transfer heat between two fluids, working like a baton-passing relay race runner. They play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of the refrigeration cycle, ensuring that your home stays cool and your energy bills don’t go through the roof.
Basic Components of a Refrigeration Cycle
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of how a refrigeration cycle with heat exchanger works, let’s get familiar with the basic components of the cycle. Don’t worry, it’s not rocket science!
Compressor
The compressor is like the heart of your refrigeration system. Its job is to pump up the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. Think of it as a powerlifter, making the refrigerant strong and ready for action. There are different types of compressors, such as reciprocating, rotary, scroll, and screw compressors, but their main goal is the same: pump up the refrigerant!
Condenser
Next up is the condenser. You can think of it as the “cool down” station for the refrigerant. It releases heat from the refrigerant to the environment, making sure the refrigerant stays cool and collected. There are different types of condensers, like air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condensers. Each one has its own unique way of cooling down the refrigerant, but they all help maintain a chill environment for your home.
Expansion valve
After the condenser, the refrigerant heads to the expansion valve. This little guy’s job is to reduce the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, giving it a much-needed breather. It’s like a yoga teacher, helping the refrigerant relax and let go of all that built-up pressure. There are various types of expansion valves, such as thermostatic expansion valves (TXV), automatic expansion valves (AXV), and capillary tubes. Each type has its own way of helping the refrigerant find its inner zen.
Evaporator
Finally, we have the evaporator. This is where the magic happens. The evaporator’s job is to absorb heat from the surrounding space or substance, making everything nice and cool. It’s like a superhero, swooping in to save the day by keeping your home comfortable. There are different types of evaporators, like plate, finned, and shell-and-tube evaporators. Each one has its own unique way of absorbing heat, but they all work together to keep your home cool and comfy.
Types of Heat Exchangers in Refrigeration Systems
Now that we know the basics of the refrigeration cycle, let’s take a closer look at the heat exchangers that play a crucial role in this process. There are several types of heat exchangers used in refrigeration systems, each with their own advantages.
Shell and tube heat exchangers
Imagine a bunch of tubes inside a larger shell. That’s what shell and tube heat exchangers look like. They boost high efficiency, easy maintenance, and a versatile design that can be tailored to various applications. These heat exchangers are like the reliable friend you can always count on to get the job done.
Plate heat exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are made up of a stack of corrugated metal plates with gaps for fluid flow. They’re compact, offer high heat transfer efficiency, and are easy to expand if needed. These heat exchangers are like a Swiss Army knife, packing a lot of power into a small, versatile package.
Microchannel heat exchangers
Picture small, flat tubes with fins for improved heat transfer – that’s a microchannel heat exchanger. These heat exchangers are lightweight, compact, and boast high efficiency with a low refrigerant charge. They’re like the sleek, modern smartphone of heat exchangers – small, powerful, and efficient.
To learn more on heat exchangers, check out our hub page: Heat Exchangers: Easy Guide to Cooling Systems
Role of Heat Exchangers in the Refrigeration Cycle
Now that we know the different types of heat exchangers, let’s explore their roles in the refrigeration cycle. Heat exchangers are used for both subcooling and superheating, both of which help improve the efficiency of the refrigeration system.
Heat exchangers for subcooling
Subcooling is the process of cooling the refrigerant below its condensation temperature. This helps increase the cooling capacity and improve the overall efficiency of the system. To achieve subcooling, a heat exchanger is placed between the condenser and the expansion valve. It’s like giving the refrigerant an extra boost of energy to help it cool things down even more.
Heat exchangers for superheating
Superheating involves increasing the temperature of the refrigerant vapor above its saturation point. This helps protect the compressor and improves system efficiency. To achieve superheating, a heat exchanger is placed between the evaporator and the compressor. It’s like giving the refrigerant a pep talk, ensuring it’s ready to face the compressor and do its job.
Design Considerations for Heat Exchangers in Refrigeration Systems
When designing a heat exchanger for a refrigeration system, there are several important factors to consider. Let’s take a closer look at these key design considerations.
Material selection
Material selection is crucial when designing a heat exchanger. Factors such as thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and pressure and temperature limitations must be taken into account. Common materials used for heat exchangers include copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. It’s like choosing the perfect outfit for a special occasion – you want something that looks good, fits well, and is suited for the environment.
Size and configuration
Another important consideration is the size and configuration of the heat exchanger. Factors such as available space, heat transfer requirements, and pressure drop limitations play a role in the decision-making process. There are trade-offs to consider, as larger heat exchangers provide better performance but require more space and come with a higher cost. It’s like finding the perfect balance between form and function.
Maintenance and cleaning
Keeping your heat exchanger well-maintained and clean is essential for optimal heat transfer and system efficiency. Considerations include ease of disassembly, cleaning methods, and fouling resistance. It’s like taking care of a prized possession – you want to keep it clean and well-maintained so it continues to perform at its best.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Heat exchangers play a significant role in improving the energy efficiency of refrigeration systems, which is not only good for your wallet but also for the environment. Let’s take a closer look at these benefits.
Energy efficiency improvements
Heat exchangers help reduce energy consumption and operating costs in refrigeration systems. By improving the efficiency of the refrigeration cycle, they help you save money on your energy bills and contribute to a more sustainable future. There are also regulatory standards and incentives in place that encourage the use of energy-efficient refrigeration systems. It’s like being rewarded for doing the right thing for the planet.
Environmental considerations
The use of certain refrigerants can have a negative impact on the ozone layer and contribute to global warming. Fortunately, there are environmentally friendly refrigerants and heat exchangers with lower refrigerant charges that can help minimize these impacts. It’s like choosing a greener, more responsible path for the sake of our planet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat exchangers play a vital role in the refrigeration cycle, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the cooling process. By understanding the various types of heat exchangers used in refrigeration systems and the benefits of using them, we can make more informed decisions when it comes to our home cooling systems. Proper design, material selection, and maintenance are crucial for optimal performance, and by focusing on energy efficiency and environmental considerations, we can work towards a more sustainable future.
Future trends and developments
As technology continues to advance, we can expect improvements in heat exchanger design and materials, as well as in the refrigerants used in these systems. Additionally, there’s potential for integrating heat exchangers with renewable energy sources to further reduce environmental impact and improve energy efficiency. Together, we can look forward to a cooler, greener future!