If you find yourself wondering whether to focus on TXV superheat or subcooling, you are not alone. This article will guide you step-by-step, offering a comprehensive explanation of these critical terms and showing you how to navigate them with ease and understanding.
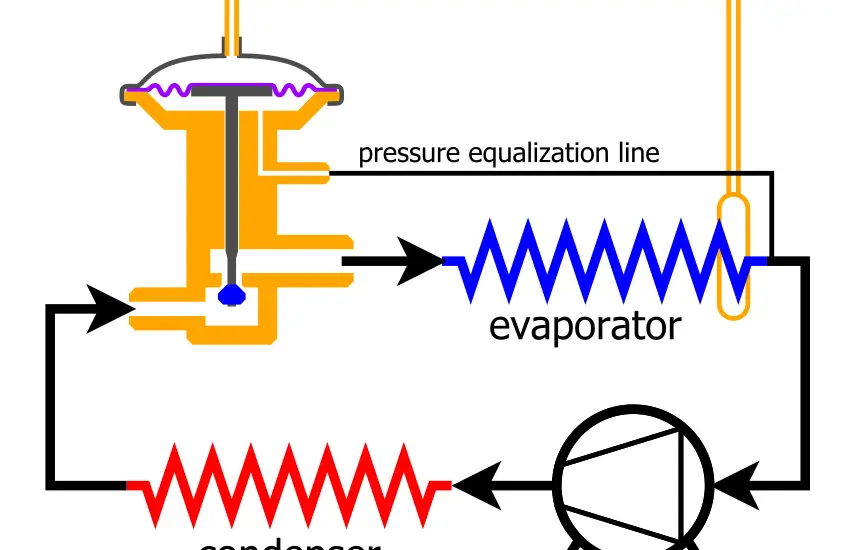
Table of Contents
Understanding Superheat
Superheat refers to the phenomenon that occurs when a vapor continues to absorb heat beyond its boiling point, resulting in a further increase in temperature. This occurrence is vital in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, particularly in the evaporator section.
In a practical sense, the superheating process starts with the refrigerant absorbing heat from the surrounding area until it reaches its boiling point and evaporates. However, this is not where it ends; the vapor continues to absorb more heat, rising in temperature, a stage known as superheating.
Superheat is measured as the difference between the actual vapor temperature and its saturation temperature at that specific pressure.
It’s essential to maintain a precise level of superheat. Too low superheat can risk liquid refrigerant entering the compressor, potentially damaging it, while too high superheat indicates that the evaporator is not being fully utilized, which can reduce the system’s efficiency.
Understanding and monitoring superheat is crucial in the tuning and maintenance of refrigeration and air conditioning systems, providing a guideline for the system’s health and efficiency.
Demystifying Subcooling
Subcooling occurs in the condenser section of your refrigeration or air conditioning system. In this process, the refrigerant releases heat into the surrounding environment, transforming from a vapor into a liquid.
The fascinating part is that this liquid continues to lose heat even after it has fully condensed, and this further cooling below the boiling point at the existing pressure is what we refer to as subcooling.
By understanding the degree of subcooling, you can glean important information about the efficiency of your condenser.
A higher degree of subcooling suggests that the refrigerant has released a greater amount of heat, which generally indicates a more efficient heat rejection process.
Just like with superheat, maintaining optimal subcooling levels is essential to ensure your system is operating efficiently and to prevent issues such as liquid hammer, which can occur if there is insufficient subcooling.
TXV Superheat or Subcooling: Which is More Important?
The question of whether TXV superheat or subcooling is more important isn’t one with a straightforward answer as it largely depends on the specific circumstances and the issue at hand.
In essence, both superheating and subcooling are pivotal in the proper functioning of a refrigeration or air conditioning system.
Superheat comes into play predominantly in the evaporator section, giving insight into its performance and indicating whether the refrigerant quantity is appropriate. Conversely, subcooling is a critical parameter when assessing the condenser’s efficiency.
As a technician or a system handler, your focus should be on maintaining optimal levels of both superheat and subcooling to ensure the system’s overall well-being and top-notch performance.
Check out these other articles…
TXV vs Piston: Which Metering Device Should You Choose?
Externally Equalized TXV: Your Ultimate Guide
Checking Superheat: The Definitive Step-by-Step Guide
Checking Superheat with TXV: In 5 Easy Steps
How to Check Superheat on TXV: Your Step-by-Step Guide
Monitoring and Adjusting TXV Superheat and Subcooling
Ensuring the efficient running of your system involves a continual process of monitoring and adjusting both the superheat and subcooling levels as necessary.
This involves utilizing tools such as pressure gauges and temperature probes to obtain accurate measurements. Moreover, understanding the optimal ranges for both superheat and subcooling in your specific system is paramount.
In need of a pressure gauge? You can check out this Yellow Jacket 42004 Series 41 Manifold Gauge on Amazon
Once the data is collected, adjustments might be needed to ensure that your system is operating within the optimal parameters. This might involve altering the refrigerant charge or adjusting the TXV to achieve the desired superheat and subcooling levels. This, in turn, helps in averting potential issues and promoting system longevity and efficiency.