Water refrigerant. Yes, you read that right. Imagine the same stuff that fills your swimming pool, quenches your thirst, and forms those pretty icicles in winter doing the job of cooling your home. Intriguing, isn’t it?
In this comprehensive piece, we will explore everything about water as a refrigerant, from its unique numbering system to its practical uses, benefits, and potential limitations. Get ready to ride the wave of knowledge.
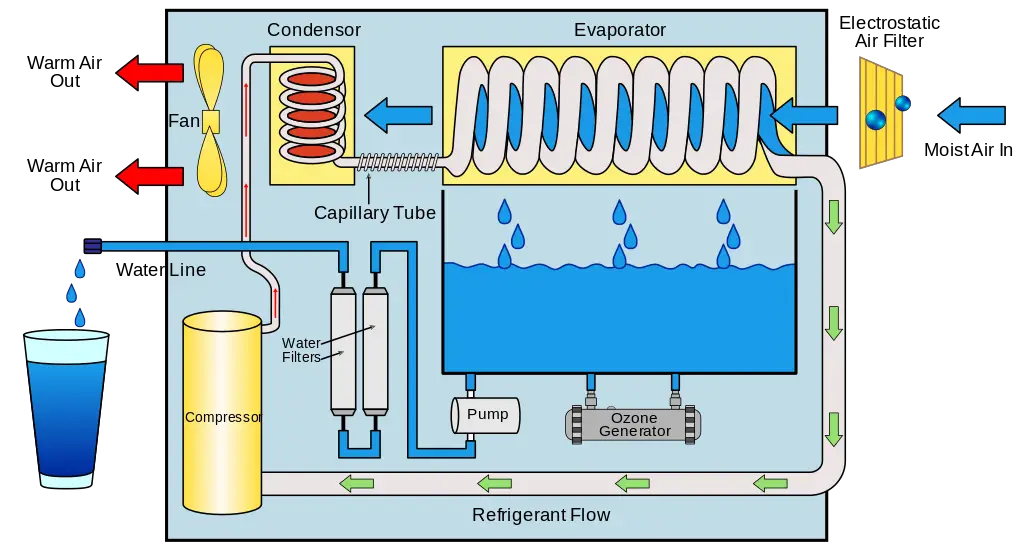
Table of Contents
What is a Water Refrigerant?
Water refrigerant? Sounds odd, doesn’t it? But it’s true. Water is not just the stuff that quenches your thirst, but also a potential game-changer in the world of refrigeration.
Understanding the Concept of Refrigerants
First things first. What’s a refrigerant? It’s a substance that absorbs heat in the environment and releases it elsewhere to cool down a space. It’s like your body sweating on a hot day to chill you out, only a tad more complex.
Introduction to Water as a Refrigerant
Now that we have a basic understanding of what refrigerants are, let’s turn our attention to how water is used as a refrigerant.
Basic Properties of Water that Make it a Potential Refrigerant
Water is an old dog with some surprising new tricks. Water’s high specific heat capacity, non-toxicity, and abundance make it an exciting candidate as a refrigerant. It’s like finding out that your favorite childhood dessert could potentially cure a common cold. Neat, isn’t it?
Historical Context of Water as a Refrigerant
While it may sound like a breakthrough, the concept of water as a refrigerant is not entirely new. Old-school engineers in the early 20th century dabbled with water for cooling purposes, like a forgotten melody making a surprising comeback in today’s pop charts.
The Water Refrigerant Number
Water has a unique place in the refrigerant numbering system, standing as a testament to its unusual and valuable properties in the world of cooling solutions.
Explanation of Refrigerant Numbering System
This system is like a ‘name tag’ for each refrigerant, helping identify its properties and composition. It’s like a secret code the industry uses to keep track of everything.
Significance of the Numbering System in Refrigerant Identification
Think of the refrigerant numbering system like a secret handshake between scientists. It helps them identify what a refrigerant is made of. Useful, right?
How Water is Numbered in the System
Here’s a cool fact. Water is identified in the refrigerant numbering system as R-718. Yes, it’s got a number, just like secret agents in old spy movies. A little cooler now, isn’t it?
Key Characteristics of the Water Refrigerant Number
What makes the water refrigerant number so special? Let’s find out as we dive into the distinct features of this unique identifier.
Understanding Water’s Unique Refrigerant Number
Why R-718, you ask? The number is derived from the molecular structure of water, which is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It’s like a unique name tag at a science convention.
Practical Implications of the Water Refrigerant Number
Having a unique refrigerant number, R-718, helps researchers and engineers quickly identify water-based refrigeration systems and differentiate them from traditional systems. It’s like having a unique badge at a festival, only this one’s for science, not fun.
Practical Use of Water as a Refrigerant
From large-scale industries to your home air conditioner, water is slowly but surely making its mark as a viable refrigerant. Let’s check out how.
Overview of Water as a Refrigerant in Different Applications
Water is more versatile than you might think. Its use as a refrigerant spans a variety of applications, each with its unique benefits and challenges.
Industrial Use Cases
Industry giants are dipping their toes into the waters of refrigeration, and why not? Water-based refrigerants are energy-efficient, non-toxic, and eco-friendly. It’s like switching from a gas-guzzling SUV to a sleek electric car – cleaner, greener, and cost-effective.
Residential Use Cases
But it’s not all about big industries. Imagine cooling your home in summer with the same water you drink and bathe in. That’s the beauty of water as a refrigerant – it’s practical, accessible, and environmentally friendly.
Pros and Cons of Using Water as a Refrigerant
Like any other refrigerant, water has its strengths and weaknesses. Let’s take a balanced look at the pros and cons of using water for cooling.
Environmental Impact
Let’s face it. Traditional refrigerants aren’t exactly a breath of fresh air for our planet. They contribute to global warming and ozone layer depletion. Water, on the other hand, poses no such threats. It’s like comparing an angry bull to a harmless butterfly – the difference is clear.
Efficiency and Performance
But how efficient is water as a refrigerant? Quite a lot, actually. Water’s high heat capacity and its ability to transfer heat make it a star performer. It’s like hiring a multi-talented actor for a movie role – they just keep surprising you.
Cost Implications
Now, let’s talk money. Water is significantly cheaper and more available than most commercial refrigerants. It’s like choosing a home-cooked meal over an expensive restaurant dish – not only is it cheaper, but it’s also more wholesome.
High Energy Input Requirement
Water-based refrigeration technologies require high energy input, which could be a limiting factor in their widespread adoption.
Costly Implementation
Water-based refrigeration technologies are currently more expensive to implement than conventional refrigeration technologies.
Lower Cooling Capacity
Furthermore, the specific nature of water as a substance means that it has a lower cooling capacity than traditional refrigerants.
Check out these other related articles…
Why Boiling Point of Refrigerant Should Be Low: Explained
XP44 Refrigerant: Your Ultimate Guide
What is Refrigerant in a Refrigerator? Your Quick 101 Guide
R718 Refrigerant: The Comprehensive Guide
R744 Refrigerant: A Comprehensive Guide
Water-Based Refrigeration Technologies
The use of water as a refrigerant is made possible through some exciting technologies. Let’s explore the systems that make this possible.
Absorption Refrigeration Systems
One of the key technologies enabling the use of water as a refrigerant is absorption refrigeration. But what exactly is it?
Working Principle
It’s a system that uses a heat source to provide the energy needed to drive the cooling process. Imagine getting a suntan while also sipping a cold drink. The sun (or any other heat source) provides the energy, while water does the cooling.
Advantages and Limitations
What’s great about absorption refrigeration? It’s energy-efficient and uses low-grade waste heat. But it’s not all sunshine and roses. The systems are complex and require a lot of components, which can drive up costs. It’s like owning a classic car – beautiful and efficient, but sometimes a bit tricky and expensive to maintain.
Adsorption Refrigeration Systems
Another important player in the water refrigeration tech field is adsorption refrigeration. How does it work and where is it used?
Working Principle
It’s like absorption’s cousin. Instead of a liquid absorbent, it uses a solid one to capture and release heat. Imagine a sponge soaking up water and then squeezing it out – that’s adsorption for you.
Advantages and Limitations
Adsorption systems are energy-efficient, especially for large-scale applications. But like all things, they have their limitations. The systems are large and the materials used for the adsorption process can be expensive. It’s like owning a yacht – fantastic for a big party, but a bit of a pocket pinch and tricky to park in your garage.
Future Perspectives on Water as a Refrigerant
What’s next for water as a refrigerant? Where’s the tide of research and development headed? Here’s a glimpse into what the future may hold for this fascinating field.
Current Research and Developments
Like explorers charting new territory, scientists are hard at work unlocking the full potential of water as a refrigerant. It’s a hot topic in labs around the world. From advancements in system design to finding more efficient ways to use water for cooling, the pace of innovation is nothing short of breathtaking.
Anticipated Trends and Potential Changes in the Industry
With the rise of green tech and focus on environmental impact, the world of water refrigerants is poised for change. What are the trends and developments we should be watching out for?
Technological Advances
Hold on to your hats, folks! The wave of technological advancements in the field of water-based refrigeration is set to revolutionize the industry. We’re talking about improved system efficiency, smart cooling solutions, and groundbreaking innovations that could transform the way we think about refrigeration. It’s like watching a sci-fi movie come to life.
Regulatory and Policy Trends
Changes in the air, and we’re not just talking about the climate. As the push for eco-friendly technologies grows stronger, we can expect policy trends to favor green refrigeration solutions like water. It’s like the winds of change blowing in the direction of a cleaner, greener future. And with regulatory bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency encouraging the use of green refrigerants, water’s time in the spotlight is certainly coming.