If you’re striving to thoroughly comprehend the concept of expansion valve pressure drop, this guide will serve as a valuable resource. We’ll delve deeply into what it is, why it’s crucial, how to measure it, and the factors that can influence it.
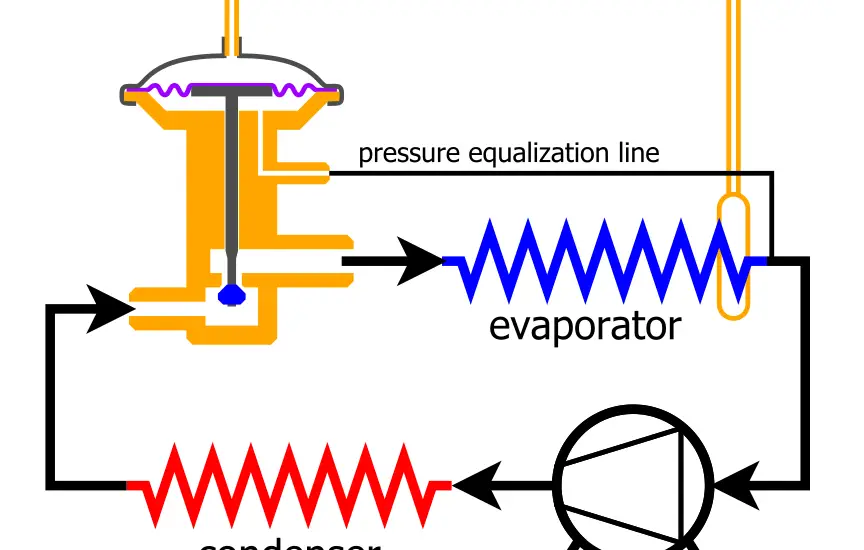
Table of Contents
What is Expansion Valve Pressure Drop?
The expansion valve pressure drop is an essential concept in thermodynamics, specifically in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. To break it down in simplest terms, it’s the difference in pressure levels before and after a refrigerant goes through an expansion valve.
This valve acts as a pressure-reducing mechanism, allowing the refrigerant to move from a high-pressure zone to a low-pressure zone in the system. The pressure “drop” is the quantitative measure of this transition.
Imagine a water slide at a pool. The top of the slide has high water pressure, and the bottom has low water pressure. The slide itself serves as the “expansion valve,” and the difference in water pressure from top to bottom represents the “pressure drop.”
Similarly, in an HVAC system, the expansion valve facilitates the transition of the refrigerant by reducing its pressure, making it ready for the next stage of the refrigeration cycle.
Why is It Important?
The significance of properly understanding and managing expansion valve pressure drop is twofold:
Temperature Regulation: When the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve and the pressure drops, its temperature also decreases. This lowered temperature is crucial because it allows the refrigerant to absorb more heat when it enters the evaporator coil, thereby making the cooling process more effective.
System Efficiency: Proper pressure drop ensures that the right amount of refrigerant enters the evaporator coil. Too much or too little can strain the system, resulting in energy inefficiency and a shortened lifespan of the HVAC unit.
Without the correct expansion valve pressure drop, your HVAC system will either underperform or be overburdened, both of which can lead to increased operational costs and potential system failure.
How to Measure Expansion Valve Pressure Drop
Accurate measurement of the expansion valve pressure drop is vital for diagnosing and optimizing system performance. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide on how to do it:
Turn Off the HVAC System: For safety reasons and accurate measurement, ensure the HVAC system is turned off.
Prepare Your Tools: You’ll need two pressure gauges. Make sure these are calibrated and in good working condition.
Attach Pressure Gauges: Connect one gauge upstream (before the expansion valve) and the other downstream (after the expansion valve). Make sure the connections are secure to avoid any leakage.
You can use this HVAC Gauges 93 Refrigerant Detection Digital Manifold Gauge Set from Amazon to measure the HVAC pressure.
Turn On the HVAC System: Restart the system and let it run for about 10 minutes to reach a stable operating condition.
Record Readings: Check both pressure gauges and jot down the readings.
Calculate Pressure Drop: The pressure drop is the upstream pressure minus the downstream pressure. Use this simple formula: Pressure Drop = Upstream Pressure – Downstream Pressure.
Check out these other related articles…
How to Adjust Car AC Expansion Valve in 8 Easy Steps
Adjusting TXV Superheat: 6 Easy Steps to Follow
TXV Adjustment Clockwise: How to Do It in 5 Easy Steps
Danfoss Expansion Valve Adjustment: A Comprehensive Guide
Adjusting TXV for Subcooling: The Ultimate How-To Guide
Factors Affecting Expansion Valve Pressure Drop
Expansion valve pressure drop isn’t a static figure; it can be influenced by several variables:
Valve Size: The diameter and length of the valve can affect the pressure drop. A bigger valve typically allows for higher flow rates, which can alter the pressure drop.
Type of Refrigerant: Different refrigerants have unique thermodynamic properties. Some may cause higher or lower pressure drops than others.
Flow Rate: The speed at which the refrigerant moves through the valve can affect the pressure drop. Faster flow rates usually result in higher pressure drops.
Temperature: The temperature of the refrigerant before it enters the valve can influence how much the pressure drops. Generally, higher temperatures can lead to lower pressure drops.
Being aware of these factors enables you to troubleshoot issues or optimize your system for better performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter issues with your HVAC system, it could be related to the expansion valve pressure drop. Common problems include:
Blockages: Foreign particles can obstruct the valve, causing an unusually high or low-pressure drop.
Wear and Tear: Over time, the valve can deteriorate, affecting its performance.
Incorrect Valve Size: If the installed valve is not the correct size for your system, it can lead to inefficiencies and reduced system performance.
If you encounter any of these issues, it’s advisable to consult with a professional HVAC technician for an accurate diagnosis and repair.