If you’re looking to fully understand pressure control and expansion valve mechanisms, this article is your go-to resource. You’ll be guided through each crucial aspect, from basic definitions to maintenance tips, all structured for clear understanding, regardless of your prior knowledge.
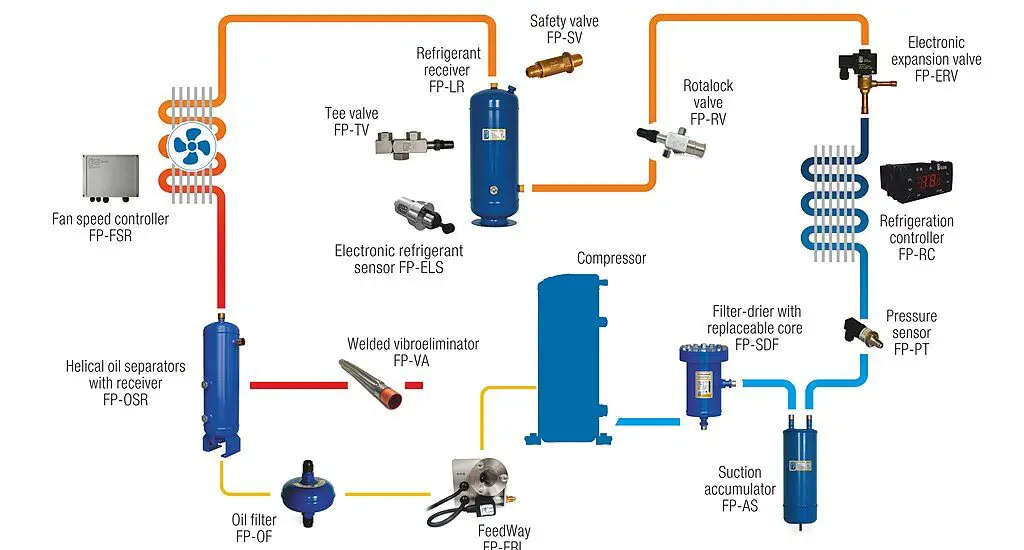
Table of Contents
What is Pressure Control and Expansion Valve?
In systems such as air conditioning, refrigeration, and some industrial processes, two types of valves play a crucial role: pressure control valves and expansion valves.
Pressure control valves monitor and regulate the pressure of the refrigerant or fluid within the system to ensure safe and efficient operation. On the other hand, expansion valves control the rate at which the refrigerant flows into the evaporator, affecting the cooling performance.
Together, these valves contribute to the system’s reliability and efficiency.
Types of Pressure Control Valves
There are two primary kinds of pressure control valves: High-Pressure Control Valves and Low-Pressure Control Valves.
High-Pressure Control Valves: These are designed to act when the system’s pressure goes above a pre-set level. If the pressure is too high, these valves restrict the flow of the refrigerant to prevent any damage or malfunction. They are typically installed on the high-pressure side of the system.
Low-Pressure Control Valves: These valves operate when the system’s pressure drops below a certain level. They open up to allow more refrigerant to flow, preventing the system from freezing or experiencing subpar cooling. These are usually found on the low-pressure side of the system.
Both types can be manually set or adjusted, and some advanced systems may even include electronic controls for finer tuning.
Types of Expansion Valves
There are several types of expansion valves, each serving a specific need:
Thermostatic Expansion Valves (TXV): These are the most commonly used and are known for their precision in regulating refrigerant flow. They adjust based on the temperature of the refrigerant, providing a very controlled flow.
Automatic Expansion Valves (AXV): These are simpler and self-operating but offer less precision. They are best suited for smaller, less complex systems.
Capillary Tubes: These are the simplest form of expansion valves and are usually found in small appliances like refrigerators. They don’t have any moving parts and operate based on the pressure differential alone.
How Does Pressure Control Work?
Pressure control valves have a built-in sensor that continuously monitors the pressure within the system.
In High-Pressure Control Valves, once the sensor detects that the pressure has risen above the pre-set limit, the valve restricts or completely stops the flow of refrigerant. This is vital to prevent mechanical failures like pipe bursts or even system explosions.
Conversely, in Low-Pressure Control Valves, if the sensor detects that the pressure has dropped below a certain point, the valve opens up to allow more refrigerant or fluid to flow. This ensures the system continues to function adequately and avoids issues like freezing or inadequate cooling.
How Does an Expansion Valve Work?
Expansion valves control the rate at which refrigerant enters the evaporator coil. When refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, its pressure drops, causing it to expand and cool. This cooling effect is crucial for the refrigeration or air conditioning process.
The type of expansion valve used can affect how precisely this process occurs. For example, a Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) adjusts its opening based on the refrigerant’s temperature, ensuring a more exact flow rate, while an Automatic Expansion Valve (AXV) operates more generically based on system pressure.
Check out these other articles…
How Expansion Valve Works in Car AC: The Complete Breakdown
Expansion Work in Thermodynamics: A Comprehensive 411 Guide
Expansion Process in Thermodynamics: Comprehensive 411 Guide
What is Thermal Expansion: A Complete 101 Guide
How Does Thermal Expansion Work: A Comprehensive 411 Guide
Choosing the Right Valve
Choosing the right pressure control and expansion valve requires a deep understanding of your system’s needs. Factors to consider include:
Type of Refrigerant: Different refrigerants have different pressure and temperature properties, so the valves need to be compatible.
System Size and Complexity: Larger, more complex systems often require more precise control, making thermostatic expansion valves and electronically controlled pressure valves a better fit.
Operating Conditions: If the system operates under varying conditions, valves with more dynamic control options may be necessary.
Consulting with engineers or technical experts can provide insights tailored to your specific operational needs.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Both pressure control and expansion valves require regular check-ups for efficient operation.
For pressure control valves, look for signs of wear and tear or leakage. For expansion valves, inconsistencies in cooling or frost formation can indicate issues.
Regular cleaning, adjustments, and occasionally, replacements, are essential for long-term reliability.