The expansion valve in refrigerator systems is an essential component that plays a pivotal role in the cooling process. In this article, you’ll learn step-by-step about its function, how it works, and why it’s crucial for the efficiency of your refrigeration system.
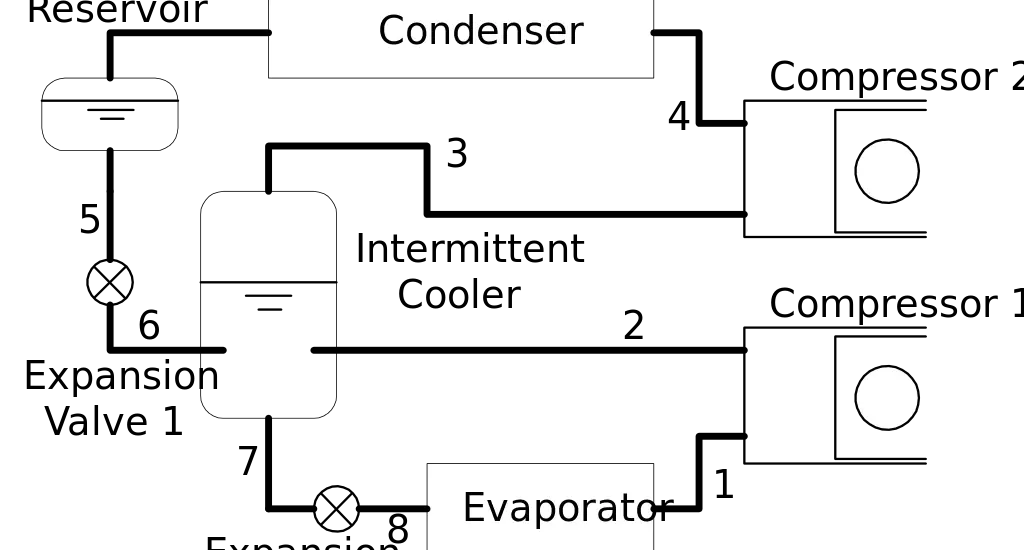
Table of Contents
What is the Expansion Valve in Refrigerator?
The expansion valve, often referred to as a throttling device, is tasked with regulating the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. Its primary function is to reduce the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, enabling it to evaporate and absorb heat from its surroundings. This process ensures that the items within your refrigerator remain cold and fresh.
How Does the Expansion Valve in Refrigerators Work?
The expansion valve in refrigerators is a complex component that operates based on the pressure and temperature of the evaporator. As the refrigerant makes its way through the valve, it experiences a rapid drop in pressure, which in turn results in a decrease in temperature.
This colder refrigerant, now at a state that allows for optimal heat absorption, flows into the evaporator. As it moves, it draws heat from the refrigerator’s interior, ensuring your stored items remain chilled.
Types of Expansion Valves Used in Refrigeration Systems
Several types of expansion valves are employed in refrigeration systems, all designed to serve the fundamental purpose of cooling the refrigerant:
Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TEV): This type of valve senses the temperature of the refrigerant as it exits the evaporator. It then adjusts the refrigerant flow based on this temperature, ensuring a consistent cooling effect.
Capillary Tube: A simple yet effective design, this long, narrow tube allows the refrigerant to flow through it. The design ensures a pressure drop, which results in the desired cooling effect.
Automatic Expansion Valve: This self-regulating valve maintains a constant pressure within the evaporator, ensuring a consistent temperature throughout the refrigeration cycle.
Significance of the Expansion Valve
The importance of the expansion valve in a refrigeration system cannot be overstated. Without it, the refrigerant would not experience the necessary drop in temperature, rendering the refrigerator virtually ineffective.
Furthermore, a correctly functioning valve ensures your refrigerator operates at optimal efficiency, using minimal energy and reducing wear and tear on other components. This efficiency not only reduces energy bills but also contributes to a longer lifespan for your appliance.
Common Issues and Solutions
Despite its critical role, the expansion valve is not immune to problems:
Sticking: Debris or contamination can cause the valve to stick, impeding its function.
Wear and Tear: Over time, the valve’s components may wear down, reducing its efficiency.
Improper Cooling: If the valve is improperly sized for the refrigerator, it might not cool efficiently.
If you encounter issues with your expansion valve, a professional’s expertise is invaluable. They can diagnose the problem, whether it’s due to contamination, wear, or other factors, and recommend appropriate measures, be it cleaning, adjustment, or replacement.
If you don’t want to go through the hassle of a repair, this SMETA Refrigerator French Door with Ice Maker on Amazon has some neat cooling features.
Check out these other related articles…
Expansion Valve in AC: Your Comprehensive Guide
Electronic Expansion Valve: Your Easy Guide
Expansion Valve Types: Your Comprehensive Guide
Expansion Valve Function: Easy 101 Guide
Expansion Valve Chiller: Your Quick 101 Guide
Deciphering the Expansion Valve Drawing
For those interested in the technicalities or perhaps involved in the maintenance of refrigeration systems, understanding the expansion valve drawing is essential.
This visual representation details the valve’s intricate design, its placement within the system, and how it interacts with other components. It provides valuable information about its dimensions, connection points, and other specific details essential for maintenance or replacement tasks.